RDEC: Integrating Regularization into Deep Embedded Clustering for Imbalanced Datasets
Paper and Code
Dec 06, 2018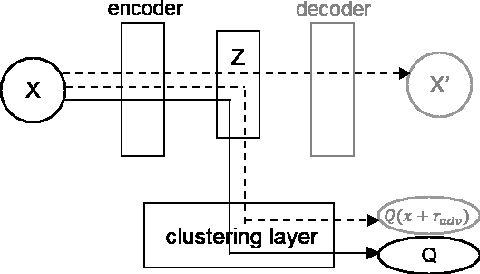
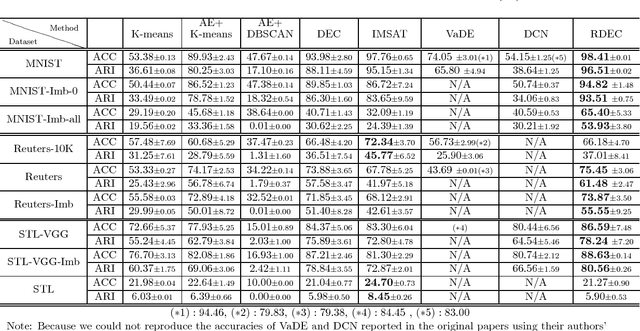
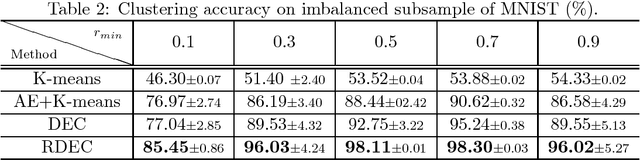
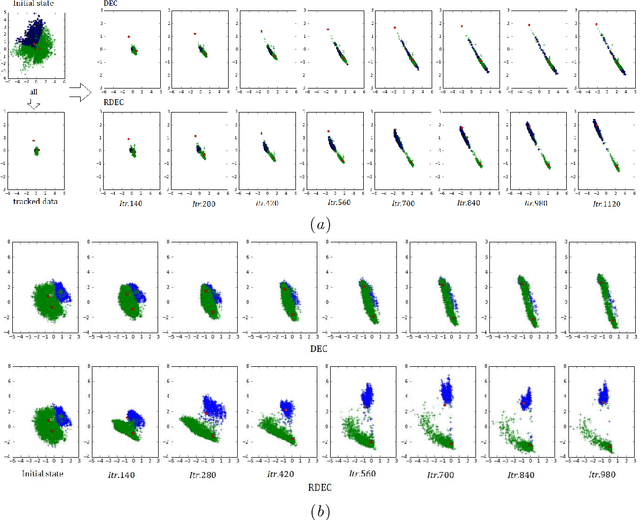
Clustering is a fundamental machine learning task and can be used in many applications. With the development of deep neural networks (DNNs), combining techniques from DNNs with clustering has become a new research direction and achieved some success. However, few studies have focused on the imbalanced-data problem which commonly occurs in real-world applications. In this paper, we propose a clustering method, regularized deep embedding clustering (RDEC), that integrates virtual adversarial training (VAT), a network regularization technique, with a clustering method called deep embedding clustering (DEC). DEC optimizes cluster assignments by pushing data more densely around centroids in latent space, but it is sometimes sensitive to the initial location of centroids, especially in the case of imbalanced data, where the minor class has less chance to be assigned a good centroid. RDEC introduces regularization using VAT to ensure the model's robustness to local perturbations of data. VAT pushes data that are similar in the original space closer together in the latent space, bunching together data from minor classes and thereby facilitating cluster identification by RDEC. Combining the advantages of DEC and VAT, RDEC attains state-of-the-art performance on both balanced and imbalanced benchmark/real-world datasets. For example, accuracies are as high as 98.41% on MNIST dataset and 85.45% on a highly imbalanced dataset derived from the MNIST, which is nearly 8% higher than the current best result.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge