Rapid Motor Adaptation for Robotic Manipulator Arms
Paper and Code
Dec 07, 2023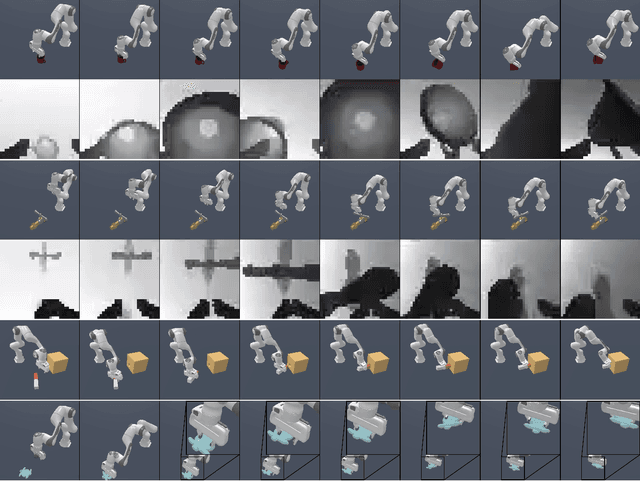



Developing generalizable manipulation skills is a core challenge in embodied AI. This includes generalization across diverse task configurations, encompassing variations in object shape, density, friction coefficient, and external disturbances such as forces applied to the robot. Rapid Motor Adaptation (RMA) offers a promising solution to this challenge. It posits that essential hidden variables influencing an agent's task performance, such as object mass and shape, can be effectively inferred from the agent's action and proprioceptive history. Drawing inspiration from RMA in locomotion and in-hand rotation, we use depth perception to develop agents tailored for rapid motor adaptation in a variety of manipulation tasks. We evaluated our agents on four challenging tasks from the Maniskill2 benchmark, namely pick-and-place operations with hundreds of objects from the YCB and EGAD datasets, peg insertion with precise position and orientation, and operating a variety of faucets and handles, with customized environment variations. Empirical results demonstrate that our agents surpass state-of-the-art methods like automatic domain randomization and vision-based policies, obtaining better generalization performance and sample efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge