Rank-One Editing of Encoder-Decoder Models
Paper and Code
Nov 23, 2022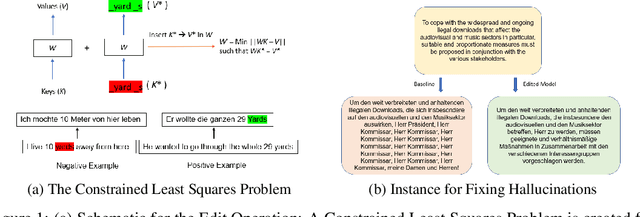
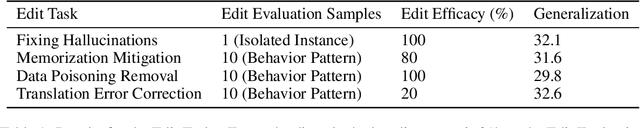
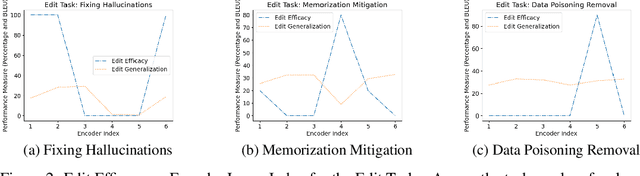

Large sequence to sequence models for tasks such as Neural Machine Translation (NMT) are usually trained over hundreds of millions of samples. However, training is just the origin of a model's life-cycle. Real-world deployments of models require further behavioral adaptations as new requirements emerge or shortcomings become known. Typically, in the space of model behaviors, behavior deletion requests are addressed through model retrainings whereas model finetuning is done to address behavior addition requests, both procedures being instances of data-based model intervention. In this work, we present a preliminary study investigating rank-one editing as a direct intervention method for behavior deletion requests in encoder-decoder transformer models. We propose four editing tasks for NMT and show that the proposed editing algorithm achieves high efficacy, while requiring only a single instance of positive example to fix an erroneous (negative) model behavior.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge