Randomized Self Organizing Map
Paper and Code
Nov 18, 2020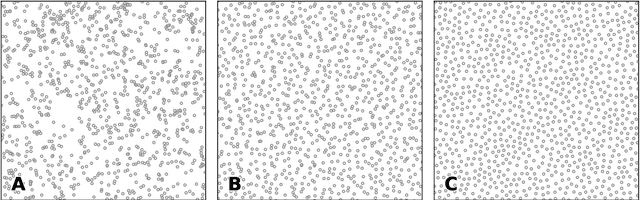
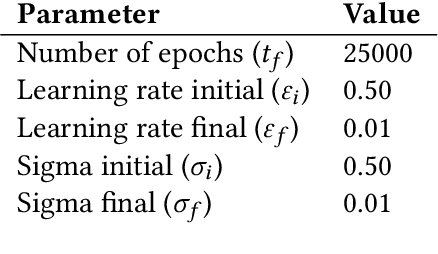
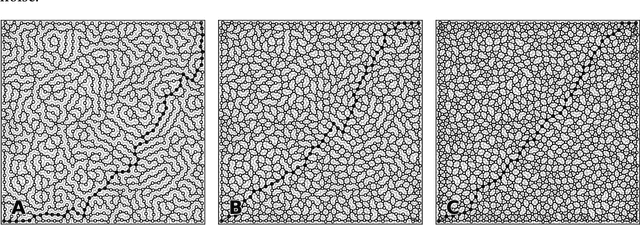
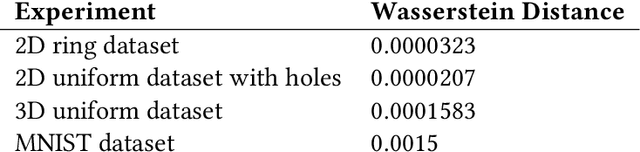
We propose a variation of the self organizing map algorithm by considering the random placement of neurons on a two-dimensional manifold, following a blue noise distribution from which various topologies can be derived. These topologies possess random (but controllable) discontinuities that allow for a more flexible self-organization, especially with high-dimensional data. The proposed algorithm is tested on one-, two- and three-dimensions tasks as well as on the MNIST handwritten digits dataset and validated using spectral analysis and topological data analysis tools. We also demonstrate the ability of the randomized self-organizing map to gracefully reorganize itself in case of neural lesion and/or neurogenesis.
* 32 pages, 19 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge