Query Learning with Exponential Query Costs
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2010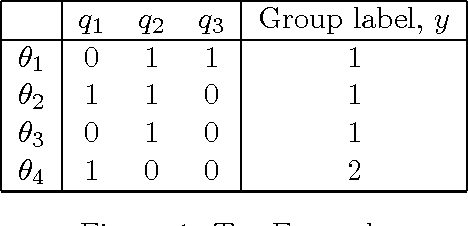
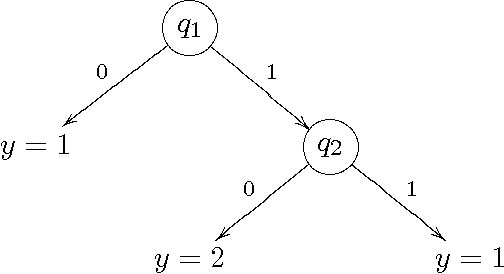
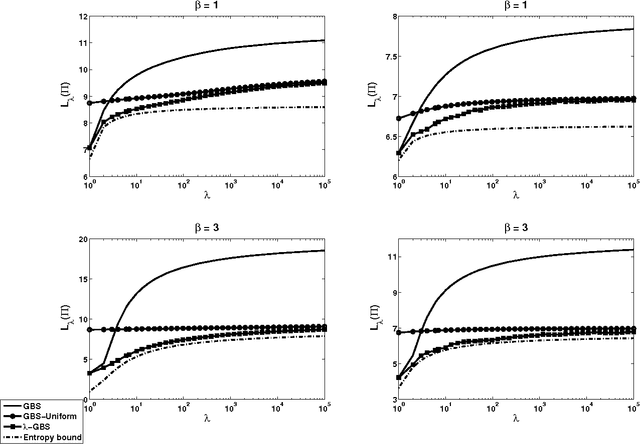
In query learning, the goal is to identify an unknown object while minimizing the number of "yes" or "no" questions (queries) posed about that object. A well-studied algorithm for query learning is known as generalized binary search (GBS). We show that GBS is a greedy algorithm to optimize the expected number of queries needed to identify the unknown object. We also generalize GBS in two ways. First, we consider the case where the cost of querying grows exponentially in the number of queries and the goal is to minimize the expected exponential cost. Then, we consider the case where the objects are partitioned into groups, and the objective is to identify only the group to which the object belongs. We derive algorithms to address these issues in a common, information-theoretic framework. In particular, we present an exact formula for the objective function in each case involving Shannon or Renyi entropy, and develop a greedy algorithm for minimizing it. Our algorithms are demonstrated on two applications of query learning, active learning and emergency response.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge