Quantum cognition beyond Hilbert space II: Applications
Paper and Code
Apr 27, 2016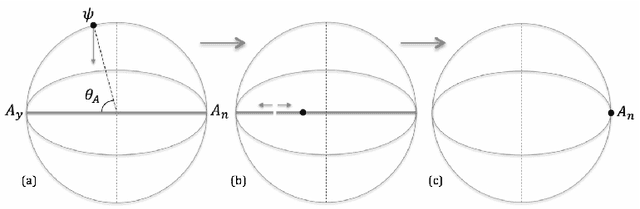
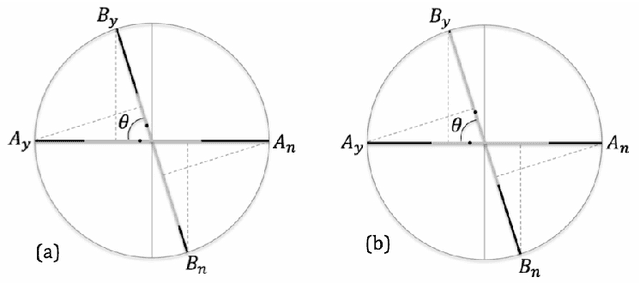
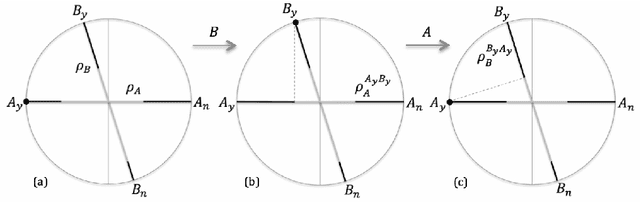
The research on human cognition has recently benefited from the use of the mathematical formalism of quantum theory in Hilbert space. However, cognitive situations exist which indicate that the Hilbert space structure, and the associated Born rule, would be insufficient to provide a satisfactory modeling of the collected data, so that one needs to go beyond Hilbert space. In Part I of this paper we follow this direction and present a general tension-reduction (GTR) model, in the ambit of an operational and realistic framework for human cognition. In this Part II we apply this non-Hilbertian quantum-like model to faithfully reproduce the probabilities of the 'Clinton/Gore' and 'Rose/Jackson' experiments on question order effects. We also explain why the GTR-model is needed if one wants to deal, in a fully consistent way, with response replicability and unpacking effects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge