Quantized Phase-Shift Design of Active IRS for Integrated Sensing and Communications
Paper and Code
Mar 10, 2023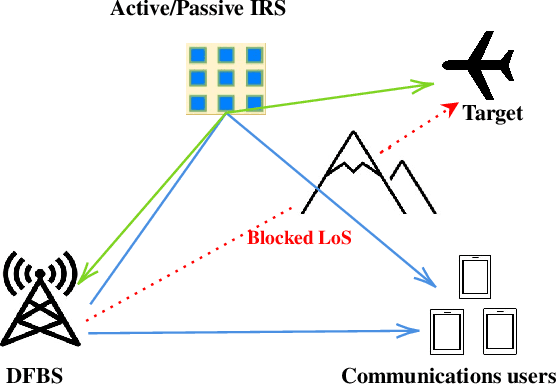
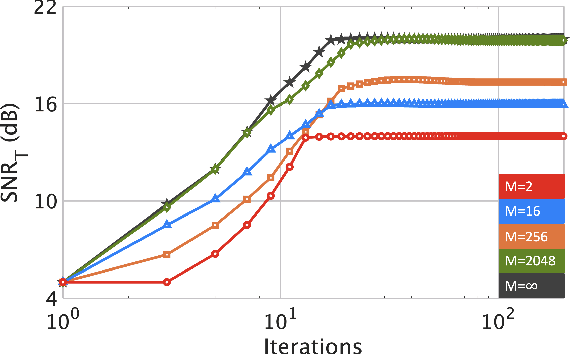
Integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) is a spectrum-sharing paradigm that allows different users to jointly utilize and access the crowded electromagnetic spectrum. In this context, intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) have lately emerged as an enabler for non-line-of-sight (NLoS) ISAC. Prior IRS-aided ISAC studies assume passive surfaces and rely on the continuous-valued phase shift model. In practice, the phase-shifts are quantized. Moreover, recent research has shown substantial performance benefits with active IRS. In this paper, we include these characteristics in our IRS-aided ISAC model to maximize the receive radar and communications signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) subjected to a unimodular IRS phase-shift vector and power budget. The resulting optimization is a highly non-convex unimodular quartic optimization problem. We tackle this via a bi-quadratic transformation to split the problem into two quadratic sub-problems that are solved using the power iteration method. The proposed approach employs the M-ary unimodular sequence design via relaxed power method-like iteration (MaRLI) to design the quantized phase-shifts. As expected, numerical experiments demonstrate that our active IRS-ISAC system design with MaRLI converges to a higher value of SNR when we increase the number of IRS quantization bits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge