Quantifying the Effect of Feedback Frequency in Interactive Reinforcement Learning for Robotic Tasks
Paper and Code
Jul 20, 2022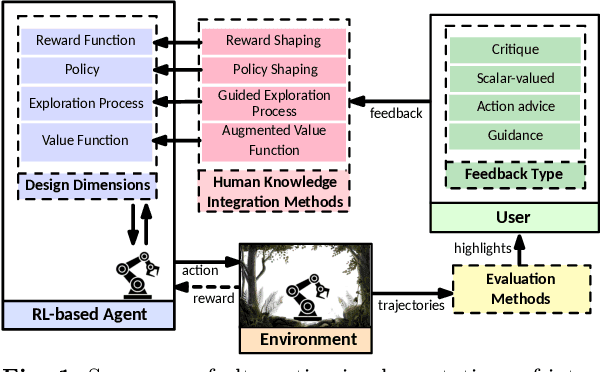


Reinforcement learning (RL) has become widely adopted in robot control. Despite many successes, one major persisting problem can be very low data efficiency. One solution is interactive feedback, which has been shown to speed up RL considerably. As a result, there is an abundance of different strategies, which are, however, primarily tested on discrete grid-world and small scale optimal control scenarios. In the literature, there is no consensus about which feedback frequency is optimal or at which time the feedback is most beneficial. To resolve these discrepancies we isolate and quantify the effect of feedback frequency in robotic tasks with continuous state and action spaces. The experiments encompass inverse kinematics learning for robotic manipulator arms of different complexity. We show that seemingly contradictory reported phenomena occur at different complexity levels. Furthermore, our results suggest that no single ideal feedback frequency exists. Rather that feedback frequency should be changed as the agent's proficiency in the task increases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge