Quantifying Circadian Desynchrony in ICU Patients and Its Association with Delirium
Paper and Code
Mar 11, 2025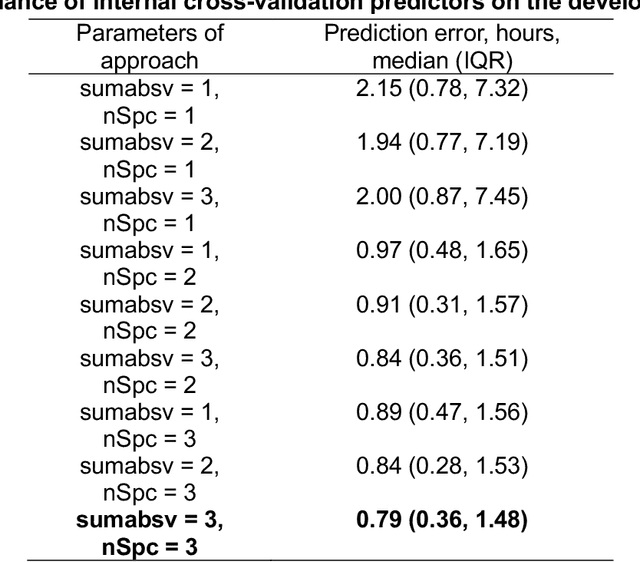
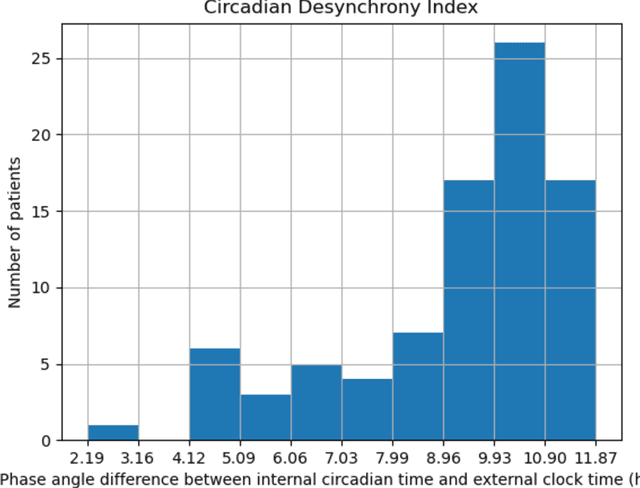
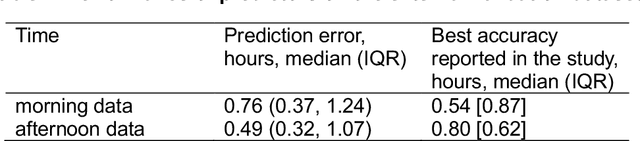

Background: Circadian desynchrony characterized by the misalignment between an individual's internal biological rhythms and external environmental cues, significantly affects various physiological processes and health outcomes. Quantifying circadian desynchrony often requires prolonged and frequent monitoring, and currently, an easy tool for this purpose is missing. Additionally, its association with the incidence of delirium has not been clearly explored. Methods: A prospective observational study was carried out in intensive care units (ICU) of a tertiary hospital. Circadian transcriptomics of blood monocytes from 86 individuals were collected on two consecutive days, although a second sample could not be obtained from all participants. Using two public datasets comprised of healthy volunteers, we replicated a model for determining internal circadian time. We developed an approach to quantify circadian desynchrony by comparing internal circadian time and external blood collection time. We applied the model and quantified circadian desynchrony index among ICU patients, and investigated its association with the incidence of delirium. Results: The replicated model for determining internal circadian time achieved comparable high accuracy. The quantified circadian desynchrony index was significantly higher among critically ill ICU patients compared to healthy subjects, with values of 10.03 hours vs 2.50-2.95 hours (p < 0.001). Most ICU patients had a circadian desynchrony index greater than 9 hours. Additionally, the index was lower in patients whose blood samples were drawn after 3pm, with values of 5.00 hours compared to 10.01-10.90 hours in other groups (p < 0.001)...
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge