Pyramid-BERT: Reducing Complexity via Successive Core-set based Token Selection
Paper and Code
Mar 27, 2022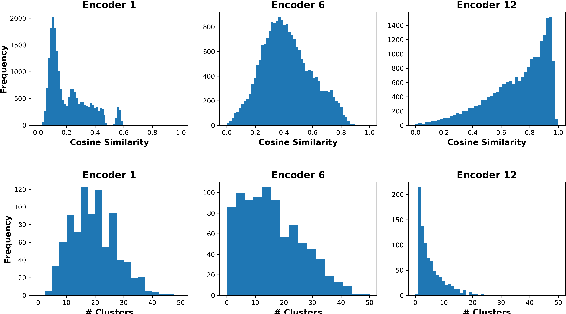
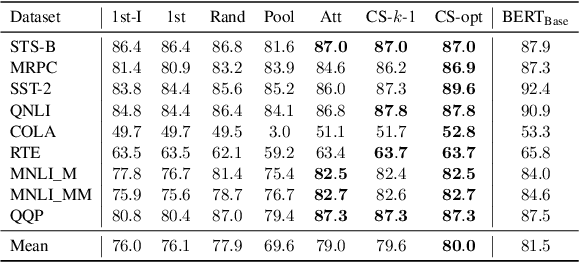
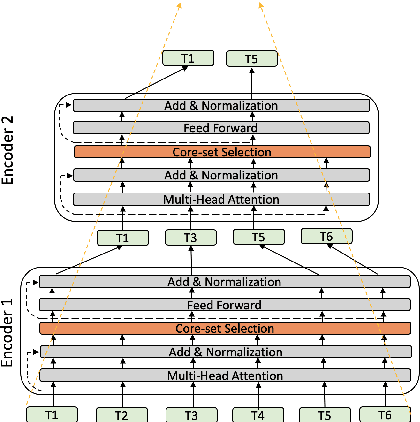
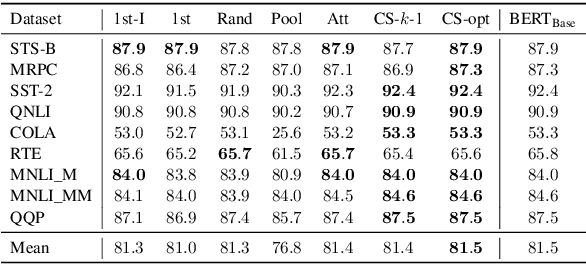
Transformer-based language models such as BERT have achieved the state-of-the-art performance on various NLP tasks, but are computationally prohibitive. A recent line of works use various heuristics to successively shorten sequence length while transforming tokens through encoders, in tasks such as classification and ranking that require a single token embedding for prediction. We present a novel solution to this problem, called Pyramid-BERT where we replace previously used heuristics with a {\em core-set} based token selection method justified by theoretical results. The core-set based token selection technique allows us to avoid expensive pre-training, gives a space-efficient fine tuning, and thus makes it suitable to handle longer sequence lengths. We provide extensive experiments establishing advantages of pyramid BERT over several baselines and existing works on the GLUE benchmarks and Long Range Arena datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge