PUF-Phenotype: A Robust and Noise-Resilient Approach to Aid Intra-Group-based Authentication with DRAM-PUFs Using Machine Learning
Paper and Code
Jul 11, 2022
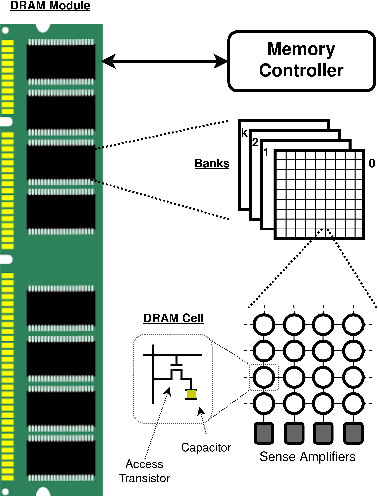


As the demand for highly secure and dependable lightweight systems increases in the modern world, Physically Unclonable Functions (PUFs) continue to promise a lightweight alternative to high-cost encryption techniques and secure key storage. While the security features promised by PUFs are highly attractive for secure system designers, they have been shown to be vulnerable to various sophisticated attacks - most notably Machine Learning (ML) based modelling attacks (ML-MA) which attempt to digitally clone the PUF behaviour and thus undermine their security. More recent ML-MA have even exploited publicly known helper data required for PUF error correction in order to predict PUF responses without requiring knowledge of response data. In response to this, research is beginning to emerge regarding the authentication of PUF devices with the assistance of ML as opposed to traditional PUF techniques of storage and comparison of pre-known Challenge-Response pairs (CRPs). In this article, we propose a classification system using ML based on a novel `PUF-Phenotype' concept to accurately identify the origin and determine the validity of noisy memory derived (DRAM) PUF responses as an alternative to helper data-reliant denoising techniques. To our best knowledge, we are the first to perform classification over multiple devices per model to enable a group-based PUF authentication scheme. We achieve up to 98\% classification accuracy using a modified deep convolutional neural network (CNN) for feature extraction in conjunction with several well-established classifiers. We also experimentally verified the performance of our model on a Raspberry Pi device to determine the suitability of deploying our proposed model in a resource-constrained environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge