Public Willingness to Get Vaccinated Against COVID-19: How AI-Developed Vaccines Can Affect Acceptance
Paper and Code
Jul 03, 2020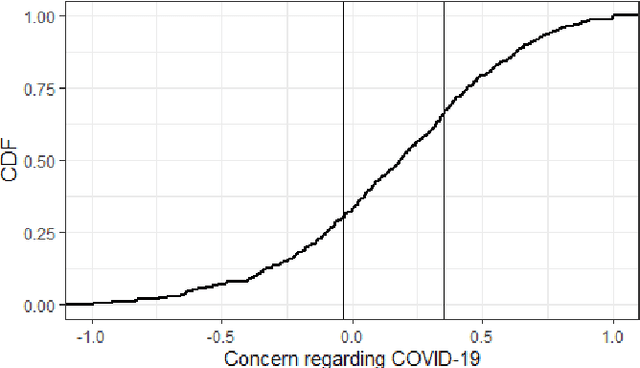
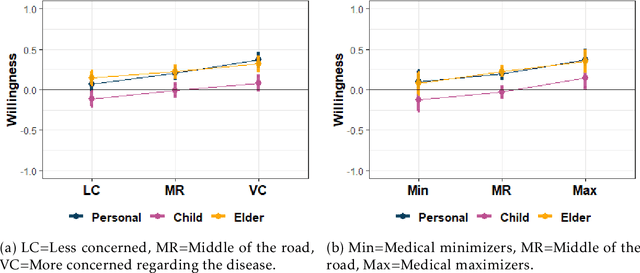
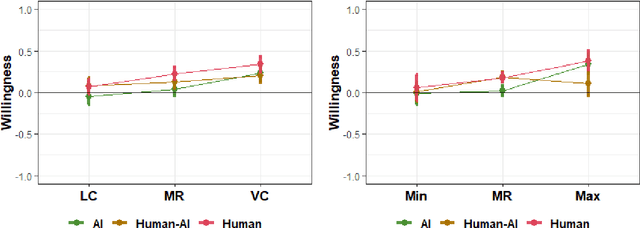
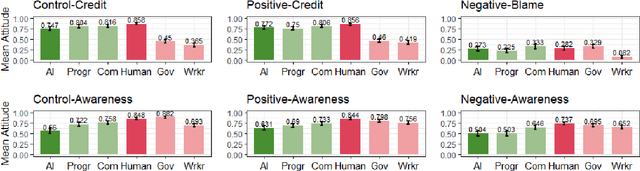
Vaccines for COVID-19 are currently under clinical trials. These vaccines are crucial for eradicating the novel coronavirus. Despite the potential, there exist conspiracies related to vaccines online, which can lead to vaccination hesitancy and, thus, a longer-standing pandemic. We used a between-subjects study design (N=572 adults in the US and UK) to understand the public willingness towards vaccination against the novel coronavirus under various circumstances. Our survey findings suggest that people are more reluctant to vaccinate their children compared to themselves. Explicitly stating the high effectiveness of the vaccine against COVID-19 led to an increase in vaccine acceptance. Interestingly, our results do not indicate any meaningful variance due to the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in developing vaccines, if these systems are described to be in use alongside human researchers. We discuss the public's expectation of local governments in assuring the safety and effectiveness of a future COVID-19 vaccine.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge