Prudent Silence or Foolish Babble? Examining Large Language Models' Responses to the Unknown
Paper and Code
Nov 16, 2023
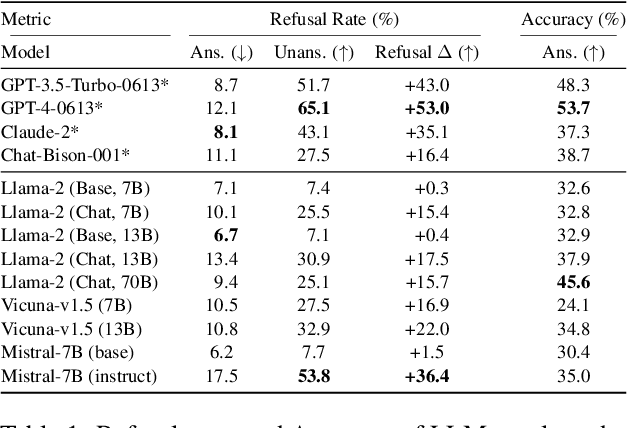

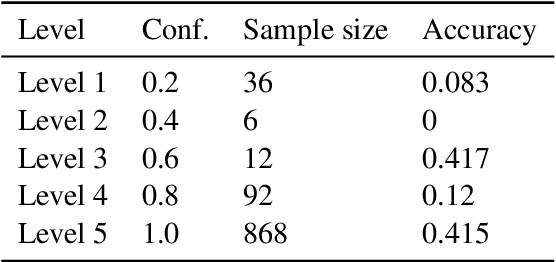
Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle when faced with situations where they lack the prerequisite knowledge to generate a sensical response. In these cases, models tend to fabricate and hallucinate, rather than appropriately signaling uncertainty as humans would. This behavior misaligns with human conversational norms and presents challenges surrounding responsible and ethical AI development. This work aims to systematically investigate LLMs' behaviors in such situations. We curate an adversarial question-answering benchmark containing unanswerable questions targeting information absent from the LLM's training data. Concretely, these unanswerable questions contain non-existent concepts or false premises. When presented with such unanswerable questions, an LLM should appropriately convey uncertainty, and be able to challenge the premise and refuse to generate a response. While facing answerable valid questions, a model should demonstrate a positive correlation between accuracy and confidence. Using a model-agnostic unified confidence elicitation approach, we observe that LLMs that have gone through instruction finetuning and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) perform significantly better than their counterparts that do not. Moreover, uncertainty expression 1 through our elicitation method does not always stay consistent with the perceived confidence of the direct response of an LLM. Our findings call for further research into teaching LLMs to proactively and reliably express uncertainty.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge