Provably optimal decision trees with arbitrary splitting rules in polynomial time
Paper and Code
Mar 03, 2025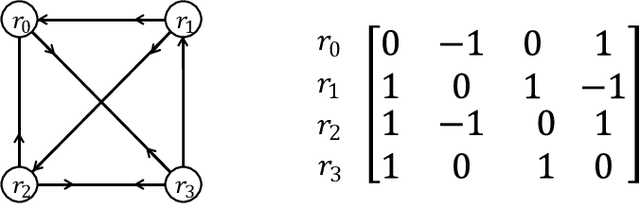
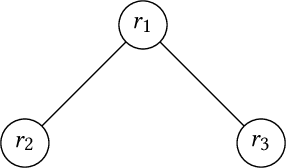
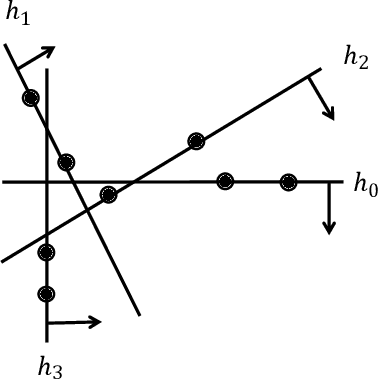
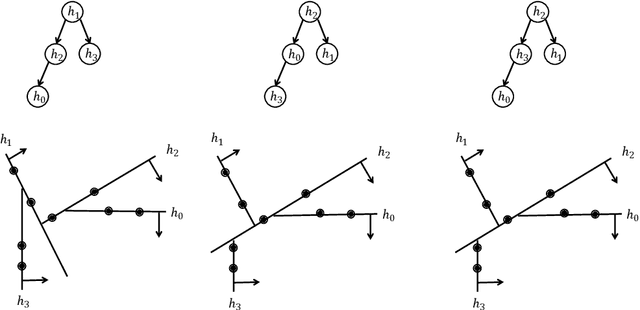
In this paper, we introduce a generic data structure called decision trees, which integrates several well-known data structures, including binary search trees, K-D trees, binary space partition trees, and decision tree models from machine learning. We provide the first axiomatic definition of decision trees. These axioms establish a firm mathematical foundation for studying decision tree problems. We refer to decision trees that satisfy the axioms as proper decision trees. We prove that only proper decision trees can be uniquely characterized as K-permutations. Since permutations are among the most well-studied combinatorial structures, this characterization provides a fundamental basis for analyzing the combinatorial and algorithmic properties of decision trees. As a result of this advancement, we develop the first provably correct polynomial-time algorithm for solving the optimal decision tree problem. Our algorithm is derived using a formal program derivation framework, which enables step-by-step equational reasoning to construct side-effect-free programs with guaranteed correctness. The derived algorithm is correct by construction and is applicable to decision tree problems defined by any splitting rules that adhere to the axioms and any objective functions that can be specified in a given form. Examples include the decision tree problems where splitting rules are defined by axis-parallel hyperplanes, arbitrary hyperplanes, and hypersurfaces. By extending the axioms, we can potentially address a broader range of problems. Moreover, the derived algorithm can easily accommodate various constraints, such as tree depth and leaf size, and is amenable to acceleration techniques such as thinning method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge