Prognostics-Informed Battery Reconfiguration in a Multi-Battery Small UAS Energy System
Paper and Code
Mar 02, 2021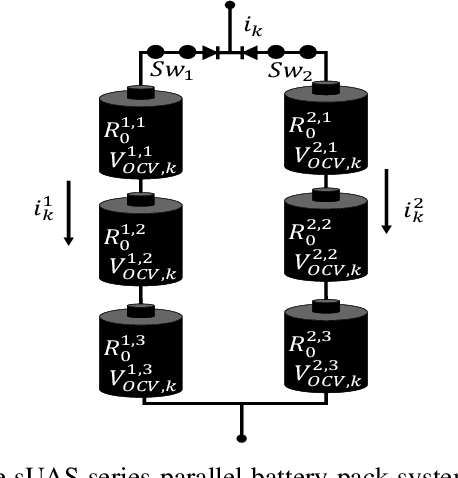
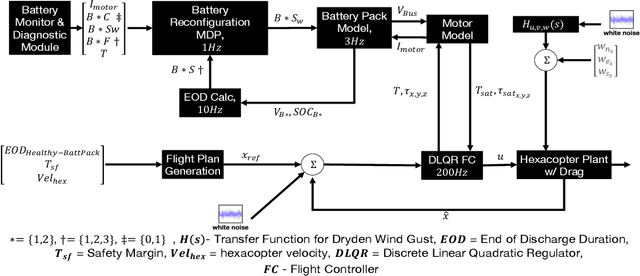
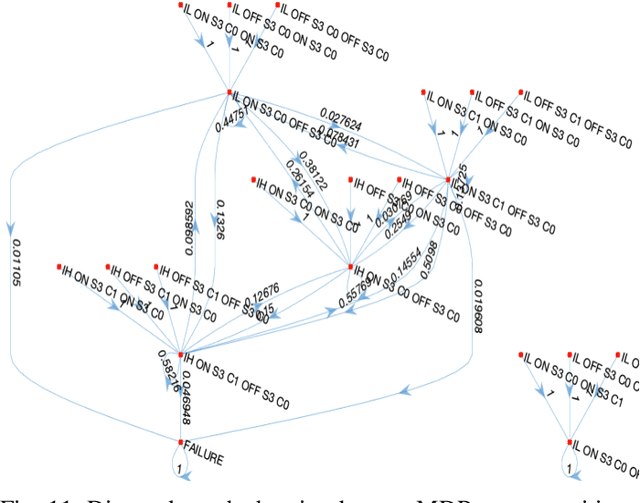

Batteries have been identified as one most likely small UAS (sUAS) components to fail in flight. sUAS safety will therefore be improved with redundant or backup batteries. This paper presents a prognostics-informed Markov Decision Process (MDP) model for managing multi-battery reconfiguration for sUAS missions. Typical lithium polymer (Lipo) battery properties are experimentally characterized and used in Monte Carlo simulations to establish battery dynamics in sUAS flights of varying duration. Case studies illustrate the trade off between multi-battery system increased complexity/weight and resilience to non-ideal battery performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge