Printable Flexible Robots for Remote Learning
Paper and Code
Jul 15, 2022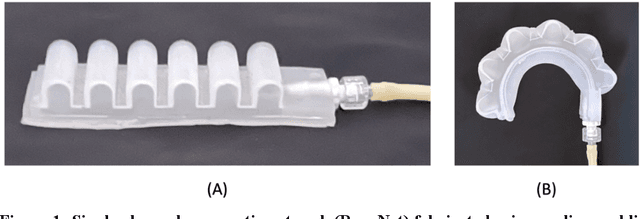
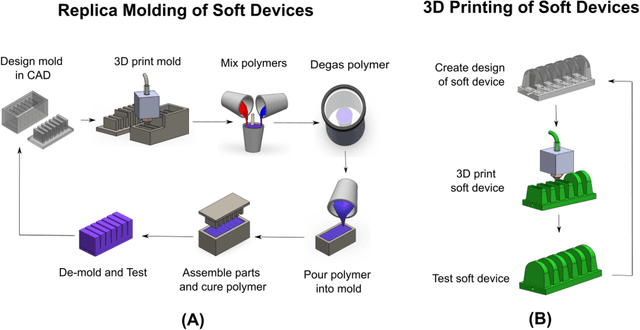
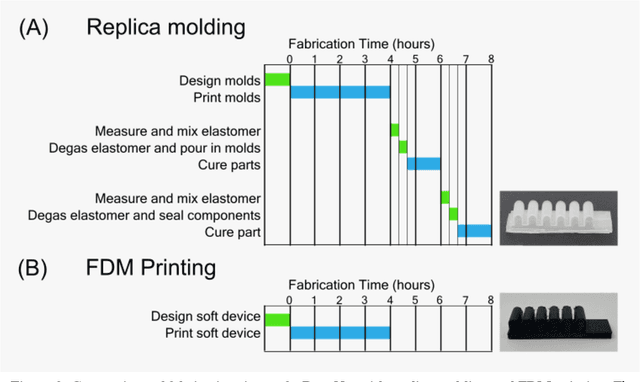
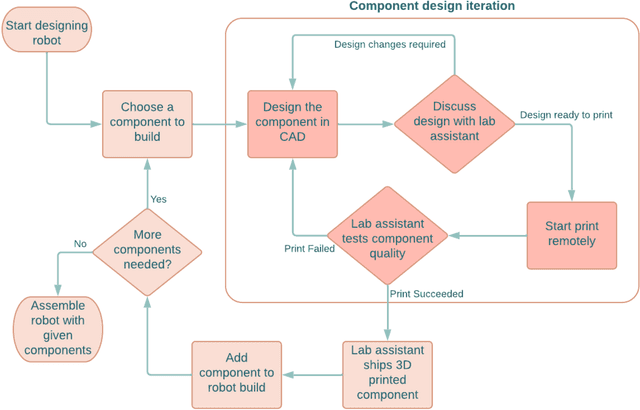
The COVID-19 pandemic has revealed the importance of digital fabrication to enable online learning, which remains a challenge for robotics courses. We introduce a teaching methodology that allows students to participate remotely in a hands-on robotics course involving the design and fabrication of robots. Our methodology employs 3D printing techniques with flexible filaments to create innovative soft robots; robots are made from flexible, as opposed to rigid, materials. Students design flexible robotic components such as actuators, sensors, and controllers using CAD software, upload their designs to a remote 3D printing station, monitor the print with a web camera, and inspect the components with lab staff before being mailed for testing and assembly. At the end of the course, students will have iterated through several designs and created fluidically-driven soft robots. Our remote teaching methodology enables educators to utilize 3D printing resources to teach soft robotics and cultivate creativity among students to design novel and innovative robots. Our methodology seeks to democratize robotics engineering by decoupling hands-on learning experiences from expensive equipment in the learning environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge