Predictive modeling of brain tumor: A Deep learning approach
Paper and Code
Dec 19, 2019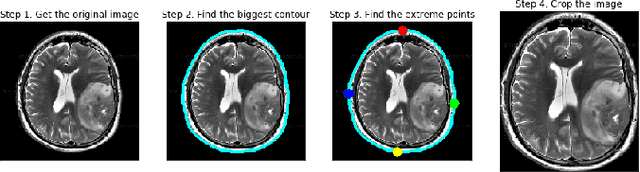
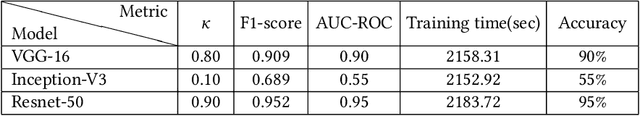
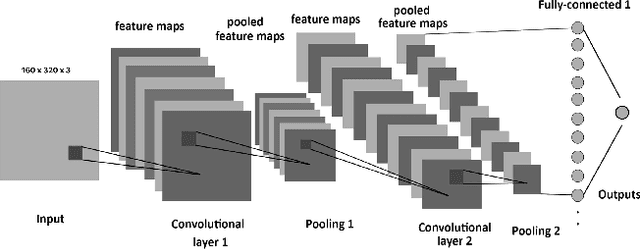
Image processing concepts can visualize the different anatomy structure of the human body. Recent advancements in the field of deep learning have made it possible to detect the growth of cancerous tissue just by a patient's brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans. These methods require very high accuracy and meager false negative rates to be of any practical use. This paper presents a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based transfer learning approach to classify the brain MRI scans into two classes using three pre-trained models. The performances of these models are compared with each other. Experimental results show that the Resnet-50 model achieves the highest accuracy and least false negative rates as 95% and zero respectively. It is followed by VGG-16 and Inception-V3 model with an accuracy of 90% and 55% respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge