Predicting Risk-of-Readmission for Congestive Heart Failure Patients: A Multi-Layer Approach
Paper and Code
Jun 10, 2013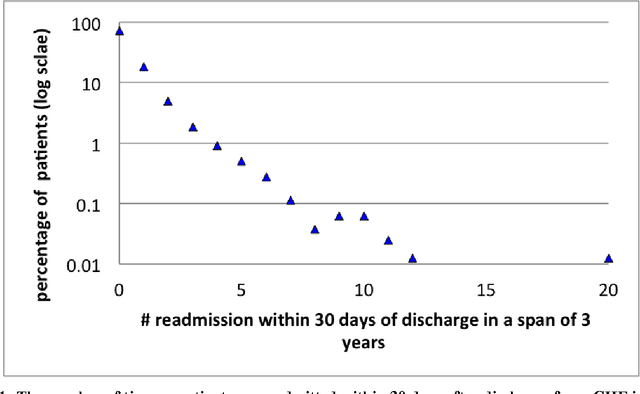

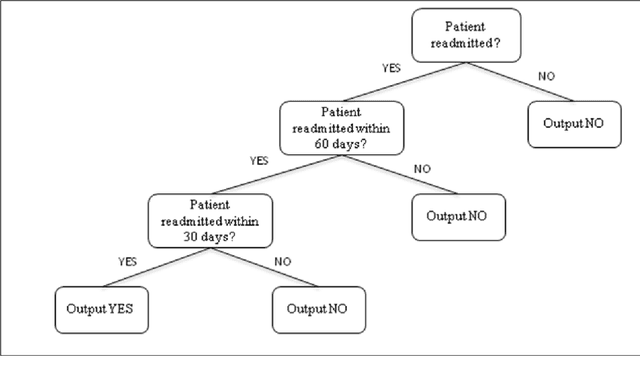

Mitigating risk-of-readmission of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) patients within 30 days of discharge is important because such readmissions are not only expensive but also critical indicator of provider care and quality of treatment. Accurately predicting the risk-of-readmission may allow hospitals to identify high-risk patients and eventually improve quality of care by identifying factors that contribute to such readmissions in many scenarios. In this paper, we investigate the problem of predicting risk-of-readmission as a supervised learning problem, using a multi-layer classification approach. Earlier contributions inadequately attempted to assess a risk value for 30 day readmission by building a direct predictive model as opposed to our approach. We first split the problem into various stages, (a) at risk in general (b) risk within 60 days (c) risk within 30 days, and then build suitable classifiers for each stage, thereby increasing the ability to accurately predict the risk using multiple layers of decision. The advantage of our approach is that we can use different classification models for the subtasks that are more suited for the respective problems. Moreover, each of the subtasks can be solved using different features and training data leading to a highly confident diagnosis or risk compared to a one-shot single layer approach. An experimental evaluation on actual hospital patient record data from Multicare Health Systems shows that our model is significantly better at predicting risk-of-readmission of CHF patients within 30 days after discharge compared to prior attempts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge