Predicting Personas Using Mechanic Frequencies and Game State Traces
Paper and Code
Mar 24, 2022
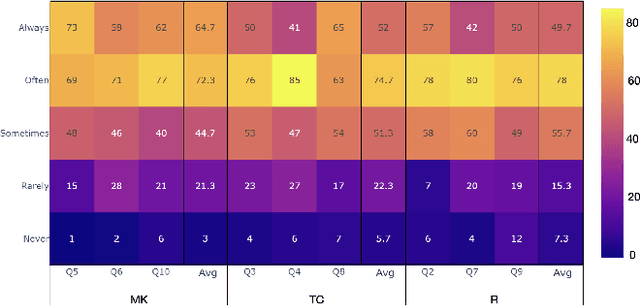
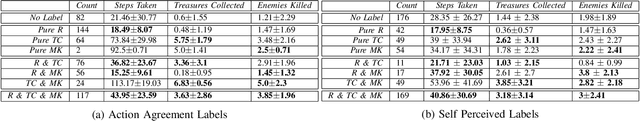
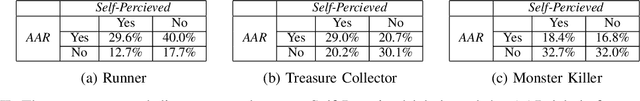
We investigate how to efficiently predict play personas based on playtraces. Play personas can be computed by calculating the action agreement ratio between a player and a generative model of playing behavior, a so-called procedural persona. But this is computationally expensive and assumes that appropriate procedural personas are readily available. We present two methods for estimating player persona, one using regular supervised learning and aggregate measures of game mechanics initiated, and another based on sequence learning on a trace of closely cropped gameplay observations. While both of these methods achieve high accuracy when predicting play personas defined by agreement with procedural personas, they utterly fail to predict play style as defined by the players themselves using a questionnaire. This interesting result highlights the value of using computational methods in defining play personas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge