Policy Gradient with Expected Quadratic Utility Maximization: A New Mean-Variance Approach in Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
Oct 03, 2020
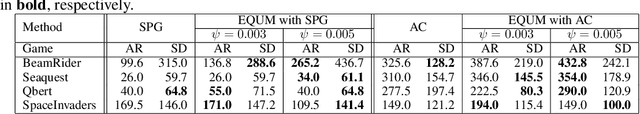

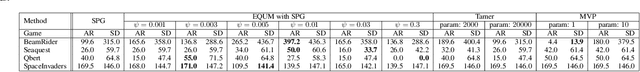
In real-world decision-making problems, risk management is critical. Among various risk management approaches, the mean-variance criterion is one of the most widely used in practice. In this paper, we suggest expected quadratic utility maximization (EQUM) as a new framework for policy gradient style reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms with mean-variance control. The quadratic utility function is a common objective of risk management in finance and economics. The proposed EQUM framework has several interpretations, such as reward-constrained variance minimization and regularization, as well as agent utility maximization. In addition, the computation of the EQUM framework is easier than that of existing mean-variance RL methods, which require double sampling. In experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework in the benchmarks of RL and financial data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge