Point Cloud Based Reinforcement Learning for Sim-to-Real and Partial Observability in Visual Navigation
Paper and Code
Jul 27, 2020
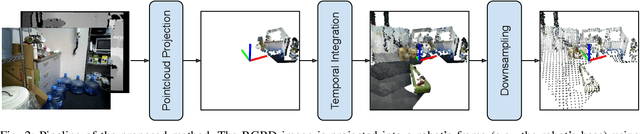

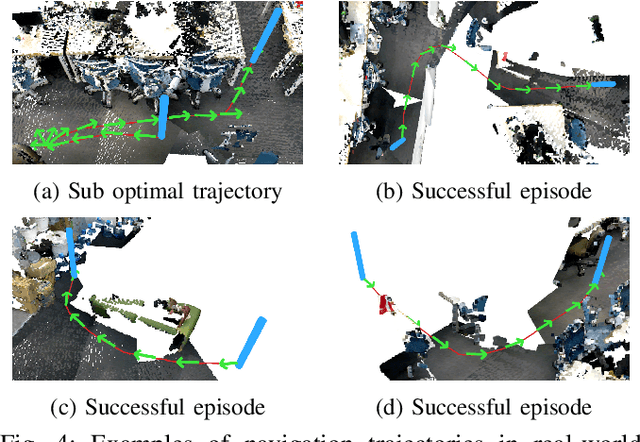
Reinforcement Learning (RL), among other learning-based methods, represents powerful tools to solve complex robotic tasks (e.g., actuation, manipulation, navigation, etc.), with the need for real-world data to train these systems as one of its most important limitations. The use of simulators is one way to address this issue, yet knowledge acquired in simulations does not work directly in the real-world, which is known as the sim-to-real transfer problem. While previous works focus on the nature of the images used as observations (e.g., textures and lighting), which has proven useful for a sim-to-sim transfer, they neglect other concerns regarding said observations, such as precise geometrical meanings, failing at robot-to-robot, and thus in sim-to-real transfers. We propose a method that learns on an observation space constructed by point clouds and environment randomization, generalizing among robots and simulators to achieve sim-to-real, while also addressing partial observability. We demonstrate the benefits of our methodology on the point goal navigation task, in which our method proves to be highly unaffected to unseen scenarios produced by robot-to-robot transfer, outperforms image-based baselines in robot-randomized experiments, and presents high performances in sim-to-sim conditions. Finally, we perform several experiments to validate the sim-to-real transfer to a physical domestic robot platform, confirming the out-of-the-box performance of our system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge