Planning Based System for Child-Robot Interaction in Dynamic Play Environments
Paper and Code
Aug 21, 2017
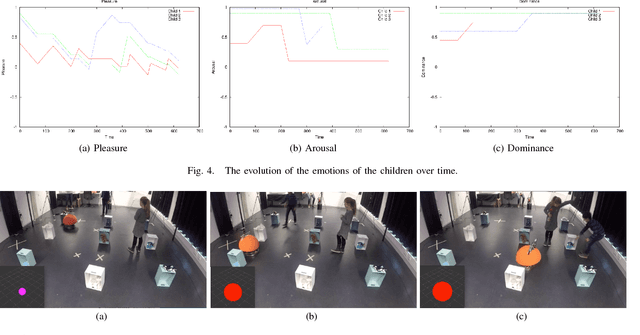
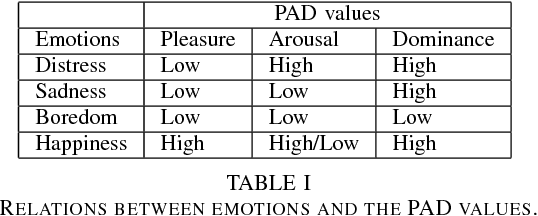
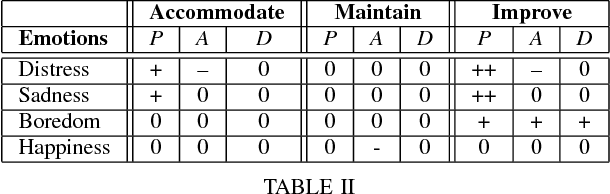
This paper describes the initial steps towards the design of a robotic system that intends to perform actions autonomously in a naturalistic play environment. At the same time it aims for social human-robot interaction~(HRI), focusing on children. We draw on existing theories of child development and on dimensional models of emotions to explore the design of a dynamic interaction framework for natural child-robot interaction. In this dynamic setting, the social HRI is defined by the ability of the system to take into consideration the socio-emotional state of the user and to plan appropriately by selecting appropriate strategies for execution. The robot needs a temporal planning system, which combines features of task-oriented actions and principles of social human robot interaction. We present initial results of an empirical study for the evaluation of the proposed framework in the context of a collaborative sorting game.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge