Physiological and Affective Computing through Thermal Imaging: A Survey
Paper and Code
Aug 27, 2019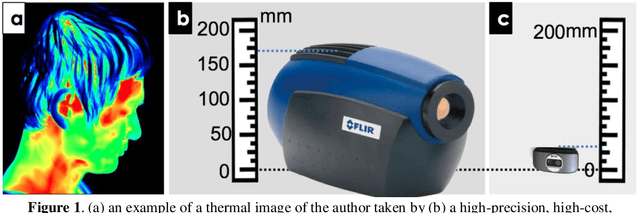
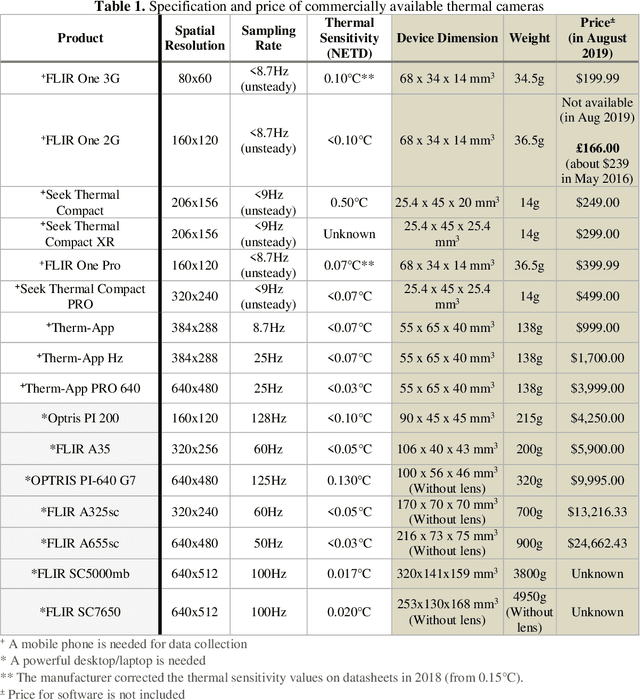
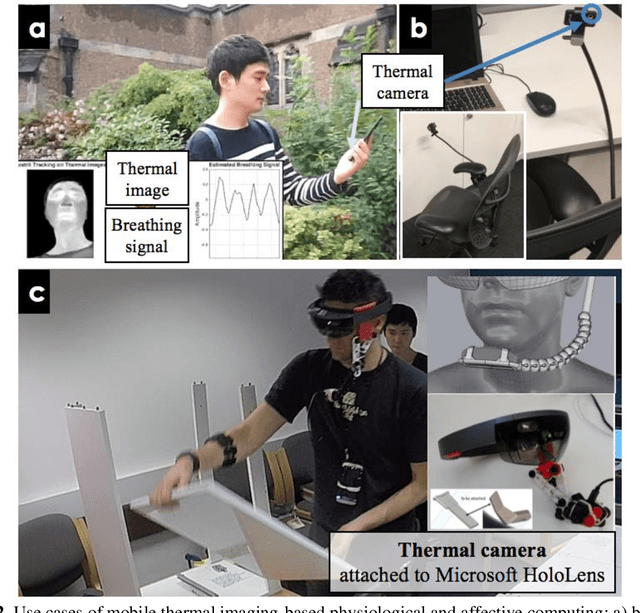
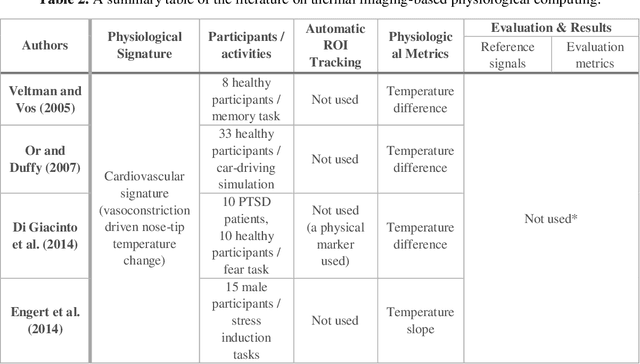
Thermal imaging-based physiological and affective computing is an emerging research area enabling technologies to monitor our bodily functions and understand psychological and affective needs in a contactless manner. However, up to recently, research has been mainly carried out in very controlled lab settings. As small size and even low-cost versions of thermal video cameras have started to appear on the market, mobile thermal imaging is opening its door to ubiquitous and real-world applications. Here we review the literature on the use of thermal imaging to track changes in physiological cues relevant to affective computing and the technological requirements set so far. In doing so, we aim to establish computational and methodological pipelines from thermal images of the human skin to affective states and outline the research opportunities and challenges to be tackled to make ubiquitous real-life thermal imaging-based affect monitoring a possibility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge