Performance Evaluation of Edge-Directed Interpolation Methods for Images
Paper and Code
Mar 26, 2013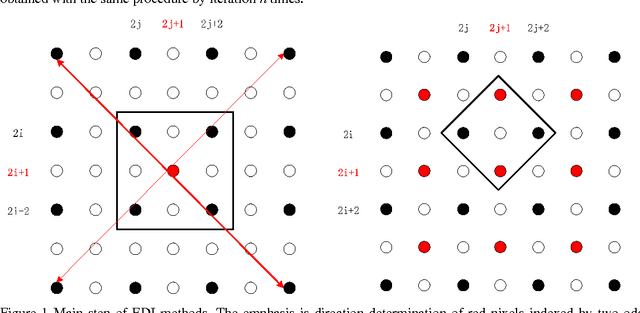
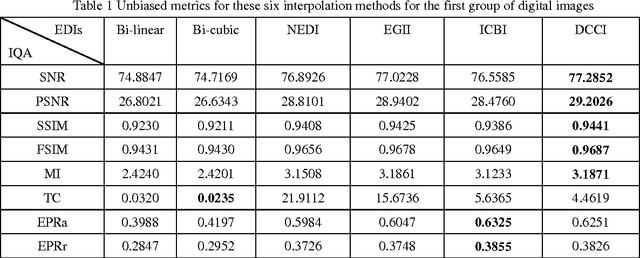
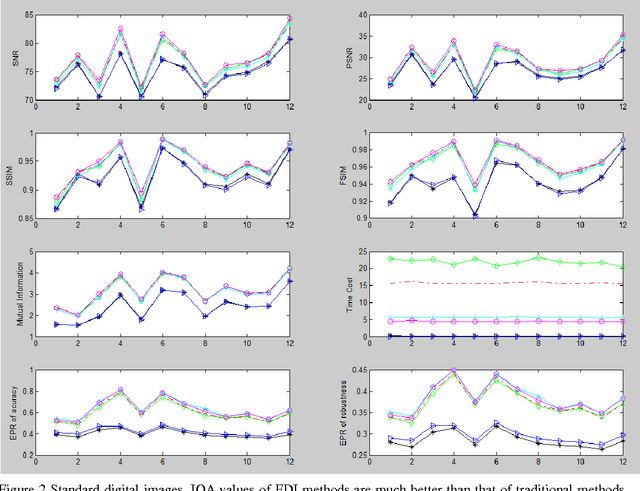
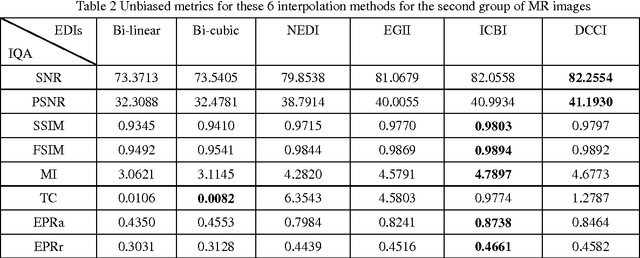
Many interpolation methods have been developed for high visual quality, but fail for inability to preserve image structures. Edges carry heavy structural information for detection, determination and classification. Edge-adaptive interpolation approaches become a center of focus. In this paper, performance of four edge-directed interpolation methods comparing with two traditional methods is evaluated on two groups of images. These methods include new edge-directed interpolation (NEDI), edge-guided image interpolation (EGII), iterative curvature-based interpolation (ICBI), directional cubic convolution interpolation (DCCI) and two traditional approaches, bi-linear and bi-cubic. Meanwhile, no parameters are mentioned to measure edge-preserving ability of edge-adaptive interpolation approaches and we proposed two. One evaluates accuracy and the other measures robustness of edge-preservation ability. Performance evaluation is based on six parameters. Objective assessment and visual analysis are illustrated and conclusions are drawn from theoretical backgrounds and practical results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge