Performance analysis of WDM in LoS communications with arbitrary orientation and position
Paper and Code
Apr 11, 2022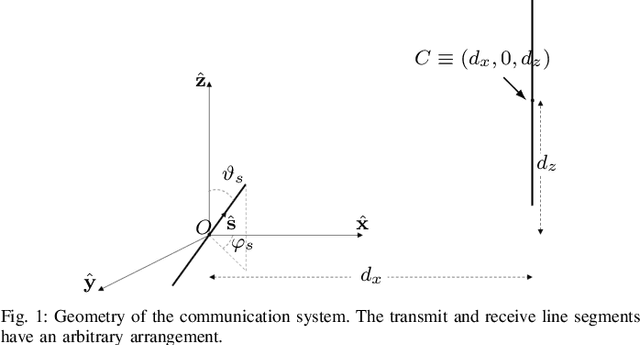

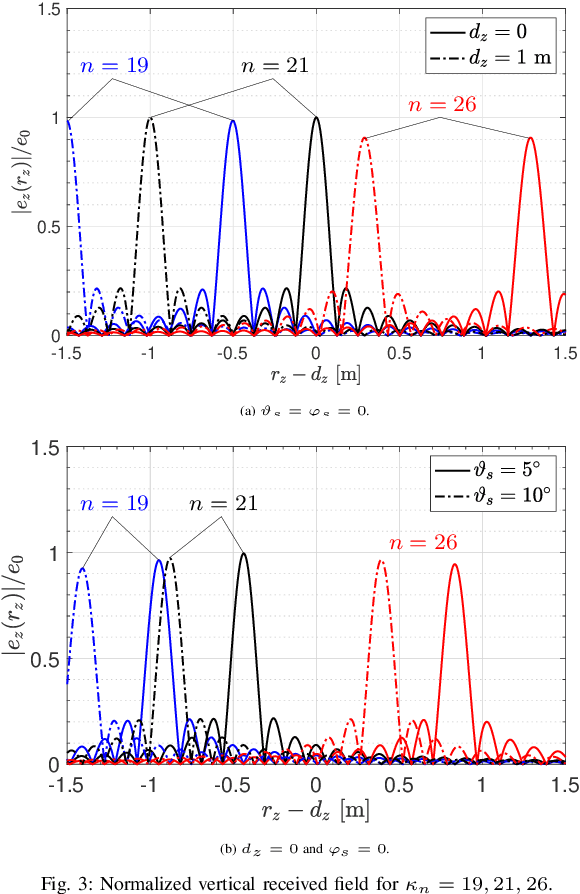

This letter focuses on the wavenumber-division-multiplexing (WDM) scheme that was recently proposed in [1] for line-of-sight communications between parallel spatially-continuous electromagnetic segments. Our aim is to analyze the performance of WDM, combined with different digital processing architectures, when the electromagnetic segments have an arbitrary orientation and position. To this end, we first show how the general electromagnetic MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) model from [1] can be particularized to the case of interest and then use numerical results to evaluate the impact of system parameters (e.g., horizontal and vertical distances, azimuth and elevation orientations). It turns out that WDM performs satisfactorily also when the transmit and receive segments are not in boresight direction of each other.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge