PatchMVSNet: Patch-wise Unsupervised Multi-View Stereo for Weakly-Textured Surface Reconstruction
Paper and Code
Mar 04, 2022
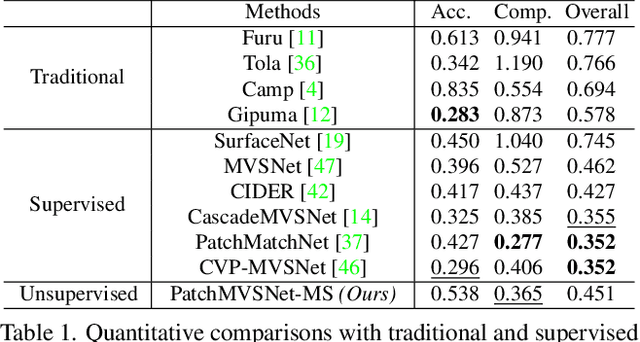
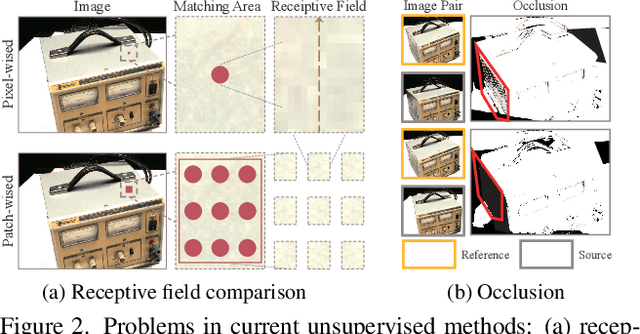

Learning-based multi-view stereo (MVS) has gained fine reconstructions on popular datasets. However, supervised learning methods require ground truth for training, which is hard to be collected, especially for the large-scale datasets. Though nowadays unsupervised learning methods have been proposed and have gotten gratifying results, those methods still fail to reconstruct intact results in challenging scenes, such as weakly-textured surfaces, as those methods primarily depend on pixel-wise photometric consistency which is subjected to various illuminations. To alleviate matching ambiguity in those challenging scenes, this paper proposes robust loss functions leveraging constraints beneath multi-view images: 1) Patch-wise photometric consistency loss, which expands the receptive field of the features in multi-view similarity measuring, 2) Robust twoview geometric consistency, which includes a cross-view depth consistency checking with the minimum occlusion. Our unsupervised strategy can be implemented with arbitrary depth estimation frameworks and can be trained with arbitrary large-scale MVS datasets. Experiments show that our method can decrease the matching ambiguity and particularly improve the completeness of weakly-textured reconstruction. Moreover, our method reaches the performance of the state-of-the-art methods on popular benchmarks, like DTU, Tanks and Temples and ETH3D. The code will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge