Partial-input baselines show that NLI models can ignore context, but they don't
Paper and Code
May 24, 2022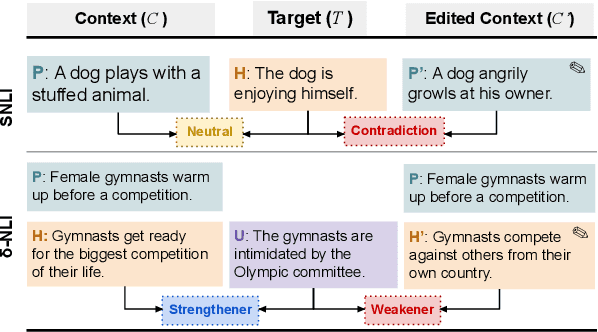


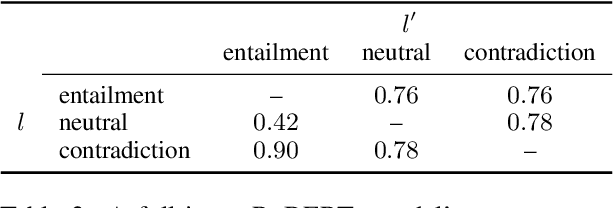
When strong partial-input baselines reveal artifacts in crowdsourced NLI datasets, the performance of full-input models trained on such datasets is often dismissed as reliance on spurious correlations. We investigate whether state-of-the-art NLI models are capable of overriding default inferences made by a partial-input baseline. We introduce an evaluation set of 600 examples consisting of perturbed premises to examine a RoBERTa model's sensitivity to edited contexts. Our results indicate that NLI models are still capable of learning to condition on context--a necessary component of inferential reasoning--despite being trained on artifact-ridden datasets.
* NAACL 2022 (Camera-Ready)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge