PageRank without hyperlinks: Structural re-ranking using links induced by language models
Paper and Code
Jan 11, 2006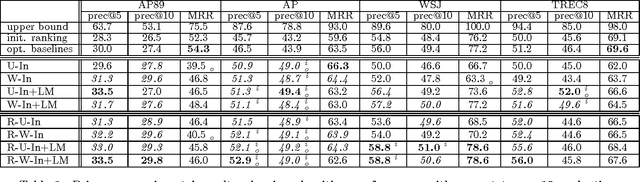
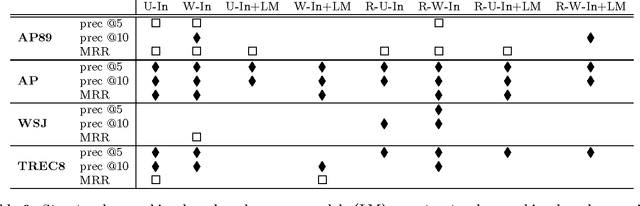
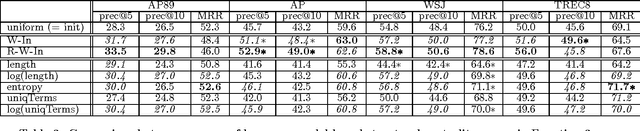
Inspired by the PageRank and HITS (hubs and authorities) algorithms for Web search, we propose a structural re-ranking approach to ad hoc information retrieval: we reorder the documents in an initially retrieved set by exploiting asymmetric relationships between them. Specifically, we consider generation links, which indicate that the language model induced from one document assigns high probability to the text of another; in doing so, we take care to prevent bias against long documents. We study a number of re-ranking criteria based on measures of centrality in the graphs formed by generation links, and show that integrating centrality into standard language-model-based retrieval is quite effective at improving precision at top ranks.
* Proceedings of SIGIR 2005, pp. 306--313
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge