Overcoming the Distance Estimation Bottleneck in Camera Trap Distance Sampling
Paper and Code
May 10, 2021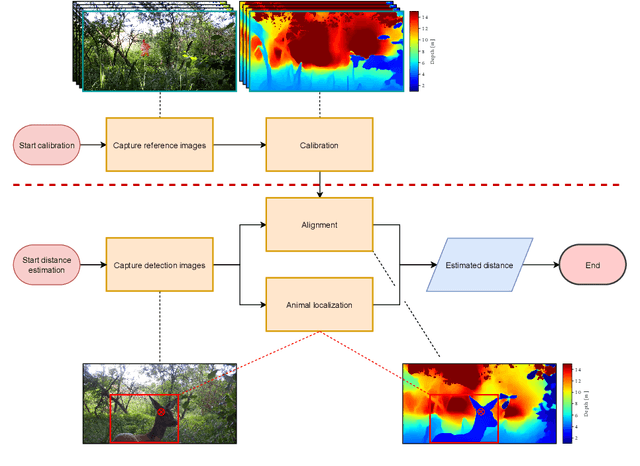
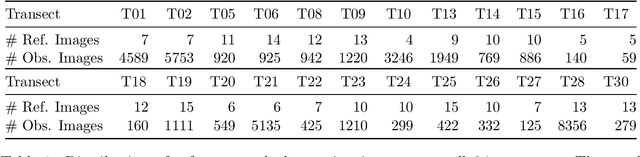

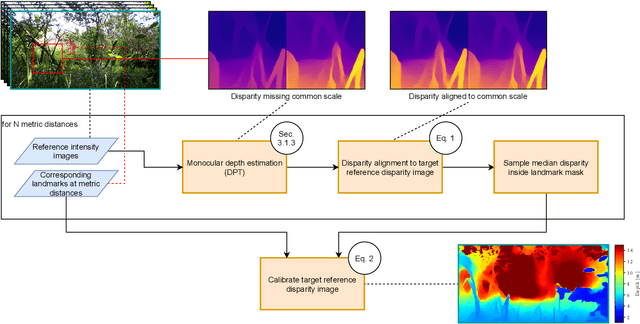
Biodiversity crisis is still accelerating. Estimating animal abundance is of critical importance to assess, for example, the consequences of land-use change and invasive species on species composition, or the effectiveness of conservation interventions. Camera trap distance sampling (CTDS) is a recently developed monitoring method providing reliable estimates of wildlife population density and abundance. However, in current applications of CTDS, the required camera-to-animal distance measurements are derived by laborious, manual and subjective estimation methods. To overcome this distance estimation bottleneck in CTDS, this study proposes a completely automatized workflow utilizing state-of-the-art methods of image processing and pattern recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge