Outrepasser les limites des techniques classiques de Prise d'Empreintes grace aux Reseaux de Neurones
Paper and Code
Jun 14, 2010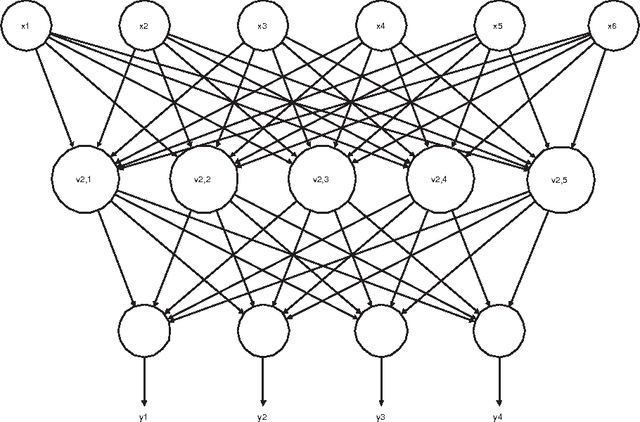
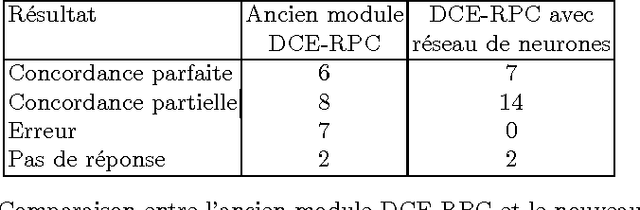
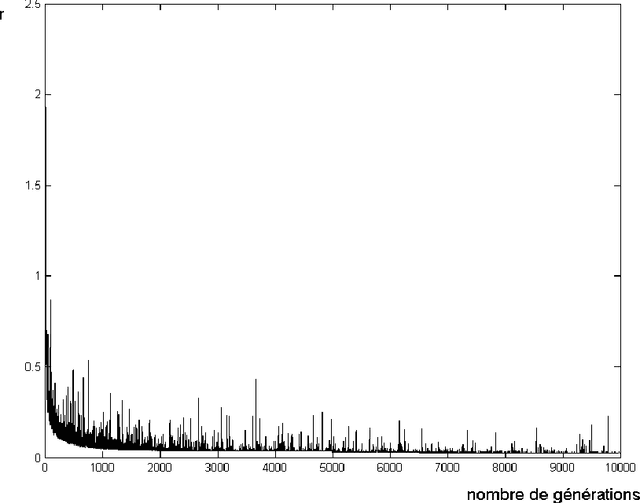
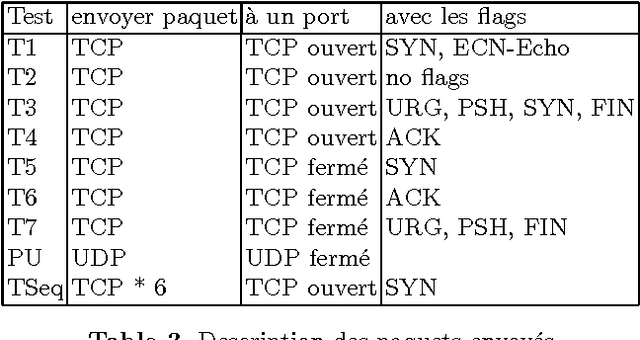
We present an application of Artificial Intelligence techniques to the field of Information Security. The problem of remote Operating System (OS) Detection, also called OS Fingerprinting, is a crucial step of the penetration testing process, since the attacker (hacker or security professional) needs to know the OS of the target host in order to choose the exploits that he will use. OS Detection is accomplished by passively sniffing network packets and actively sending test packets to the target host, to study specific variations in the host responses revealing information about its operating system. The first fingerprinting implementations were based on the analysis of differences between TCP/IP stack implementations. The next generation focused the analysis on application layer data such as the DCE RPC endpoint information. Even though more information was analyzed, some variation of the "best fit" algorithm was still used to interpret this new information. Our new approach involves an analysis of the composition of the information collected during the OS identification process to identify key elements and their relations. To implement this approach, we have developed tools using Neural Networks and techniques from the field of Statistics. These tools have been successfully integrated in a commercial software (Core Impact).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge