Out-of-Distribution Knowledge Distillation via Confidence Amendment
Paper and Code
Nov 14, 2023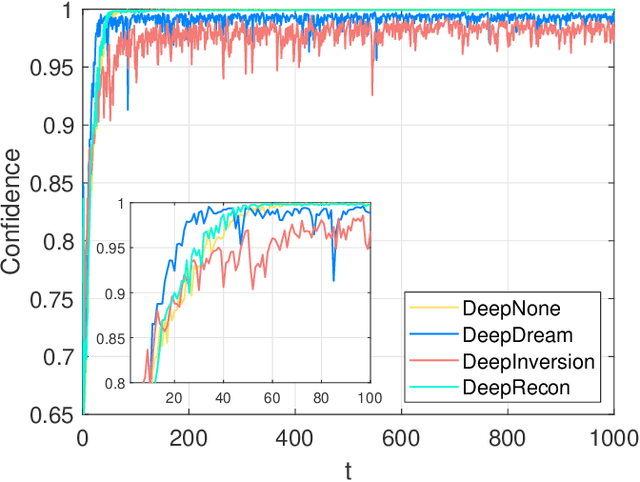
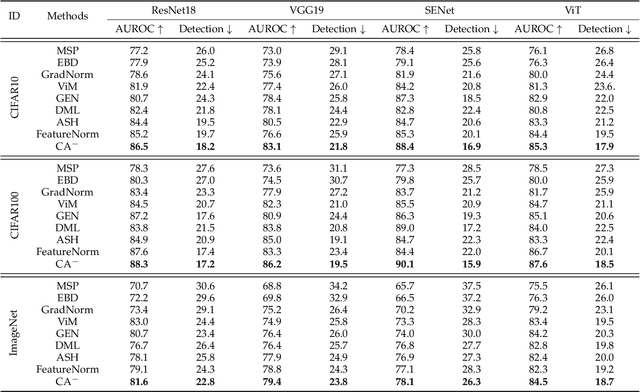
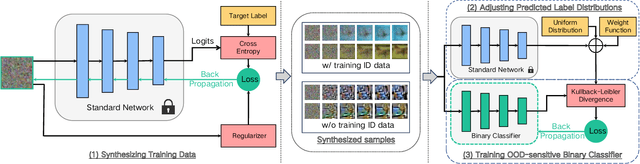
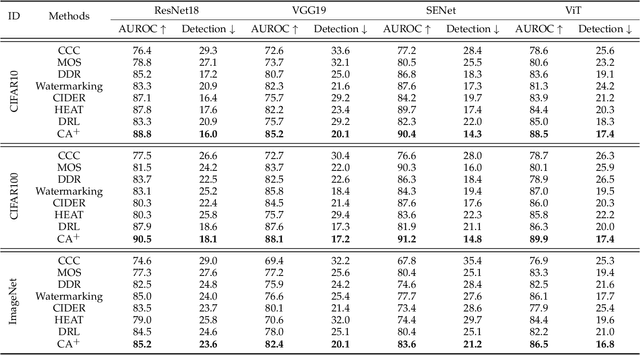
Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is essential in identifying test samples that deviate from the in-distribution (ID) data upon which a standard network is trained, ensuring network robustness and reliability. This paper introduces OOD knowledge distillation, a pioneering learning framework applicable whether or not training ID data is available, given a standard network. This framework harnesses OOD-sensitive knowledge from the standard network to craft a binary classifier adept at distinguishing between ID and OOD samples. To accomplish this, we introduce Confidence Amendment (CA), an innovative methodology that transforms an OOD sample into an ID one while progressively amending prediction confidence derived from the standard network. This approach enables the simultaneous synthesis of both ID and OOD samples, each accompanied by an adjusted prediction confidence, thereby facilitating the training of a binary classifier sensitive to OOD. Theoretical analysis provides bounds on the generalization error of the binary classifier, demonstrating the pivotal role of confidence amendment in enhancing OOD sensitivity. Extensive experiments spanning various datasets and network architectures confirm the efficacy of the proposed method in detecting OOD samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge