Oriented Boxes for Accurate Instance Segmentation
Paper and Code
Nov 27, 2019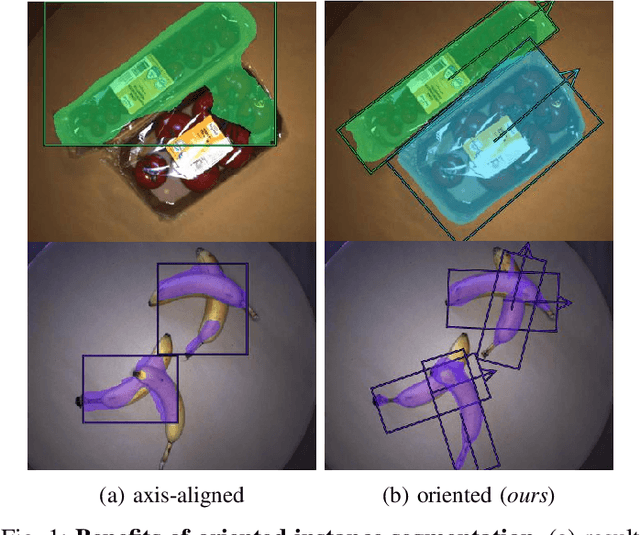
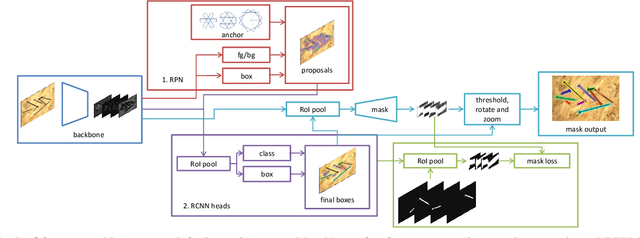
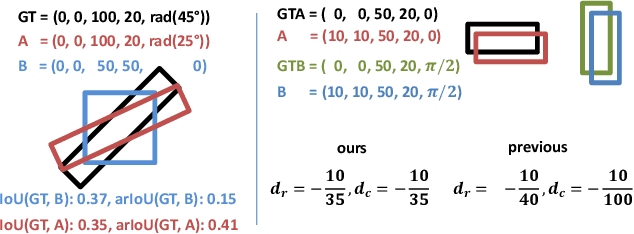
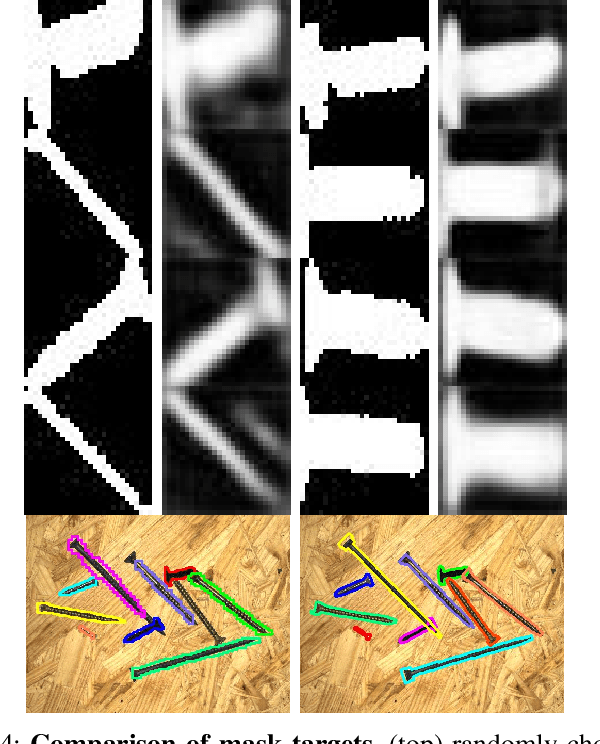
State-of-the-art instance-aware semantic segmentation algorithms use axis-aligned bounding boxes as an intermediate processing step to infer the final instance mask output. This leads to coarse and inaccurate mask proposals due to the following reasons: Axis-aligned boxes have a high background to foreground pixel-ratio, there is a strong variation of mask targets with respect to the underlying box, and neighboring instances frequently reach into the axis-aligned bounding box of the instance mask of interest. In this work, we overcome these problems and propose using oriented boxes as the basis to infer instance masks. We show that oriented instance segmentation leads to very accurate mask predictions, especially when objects are diagonally aligned, touching, or overlapping each other. We evaluate our model on the D2S and Screws datasets and show that we can significantly improve the mask accuracy by 7% and 11% mAP (14.9% and 27.5% relative improvement), respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge