Optimizing Memory Efficiency for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks on GPUs
Paper and Code
Oct 12, 2016
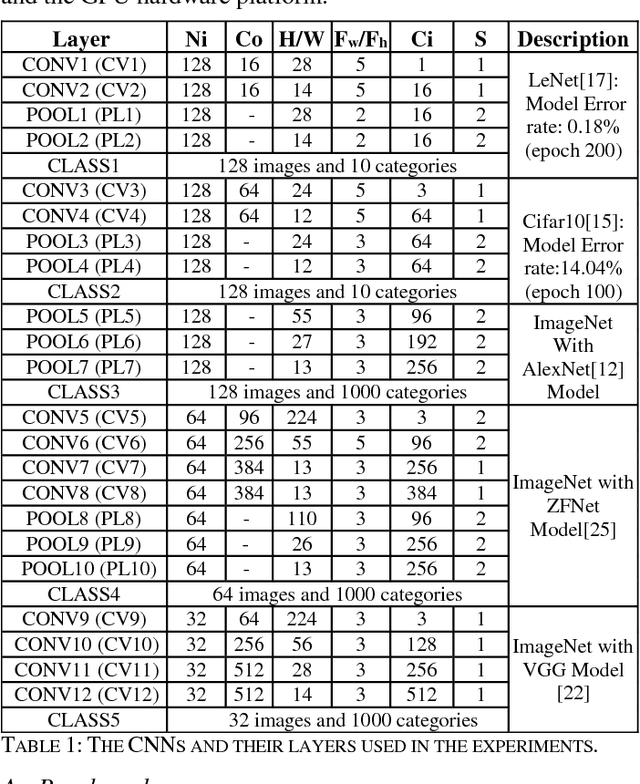
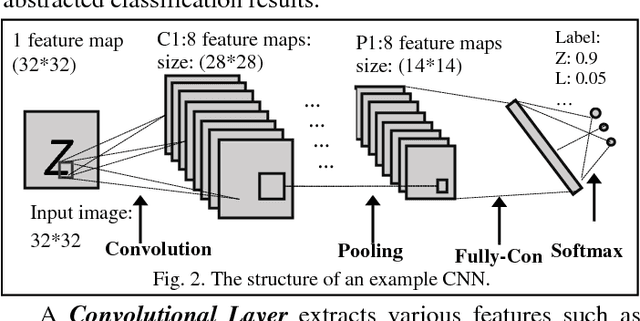
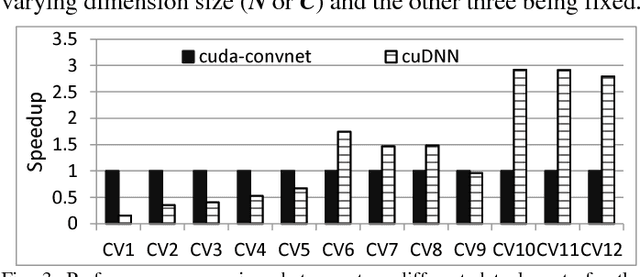
Leveraging large data sets, deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) achieve state-of-the-art recognition accuracy. Due to the substantial compute and memory operations, however, they require significant execution time. The massive parallel computing capability of GPUs make them as one of the ideal platforms to accelerate CNNs and a number of GPU-based CNN libraries have been developed. While existing works mainly focus on the computational efficiency of CNNs, the memory efficiency of CNNs have been largely overlooked. Yet CNNs have intricate data structures and their memory behavior can have significant impact on the performance. In this work, we study the memory efficiency of various CNN layers and reveal the performance implication from both data layouts and memory access patterns. Experiments show the universal effect of our proposed optimizations on both single layers and various networks, with up to 27.9x for a single layer and up to 5.6x on the whole networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge