Optimal Stochastic Evasive Maneuvers Using the Schrodinger's Equation
Paper and Code
Oct 11, 2021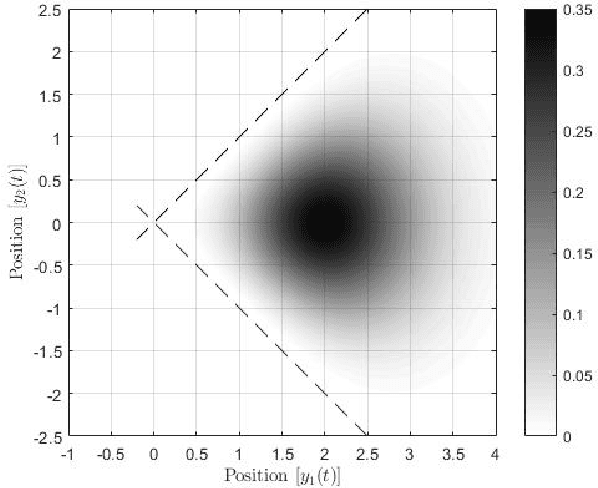
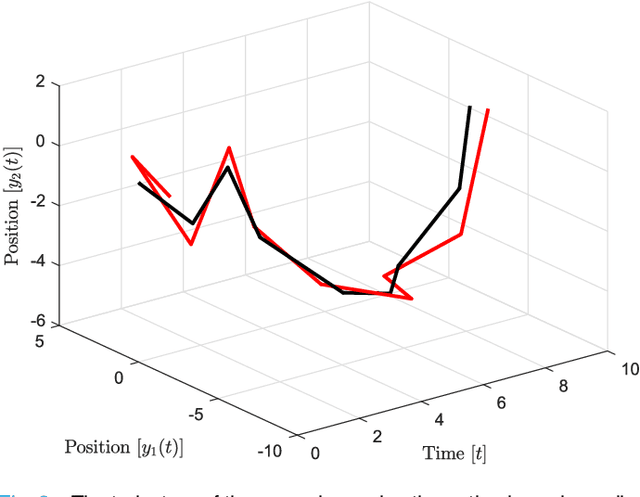
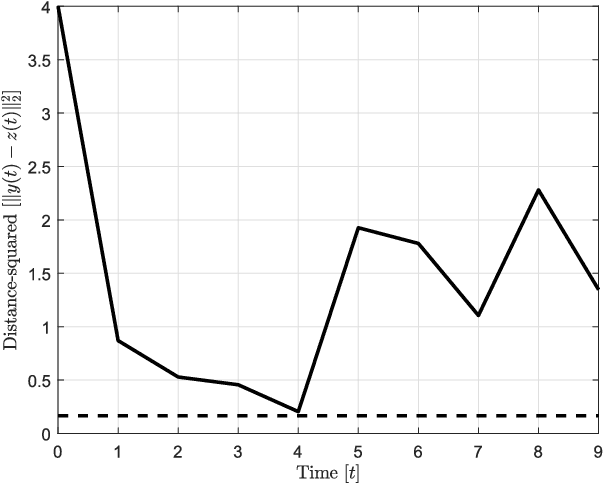
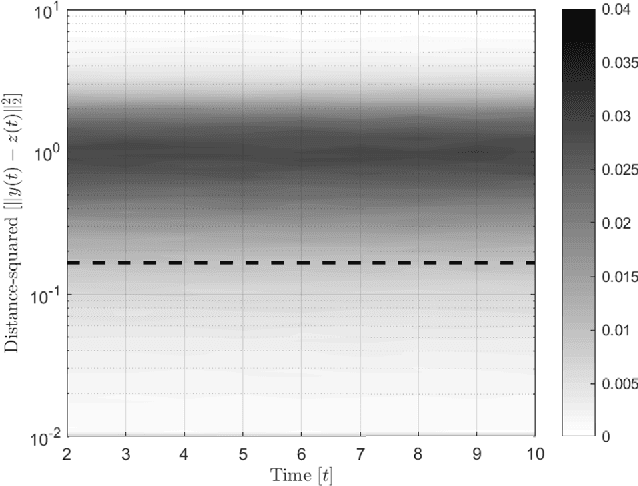
In this paper, preys with stochastic evasion policies are considered. The stochasticity adds unpredictable changes to the prey's path for avoiding predator's attacks. The prey's cost function is composed of two terms balancing the unpredictability factor (by using stochasticity to make the task of forecasting its future positions by the predator difficult) and energy consumption (the least amount of energy required for performing a maneuver). The optimal probability density functions of the actions of the prey for trading-off unpredictability and energy consumption is shown to be characterized by the stationary Schrodinger's equation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge