Optimal Automated Market Makers: Differentiable Economics and Strong Duality
Paper and Code
Feb 14, 2024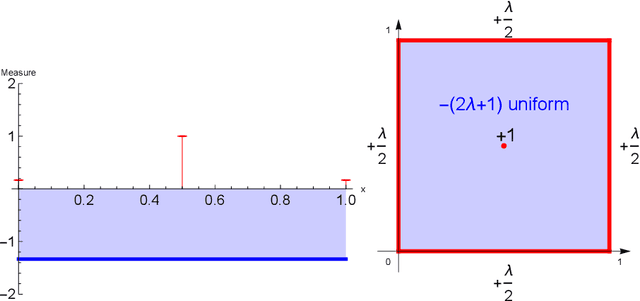
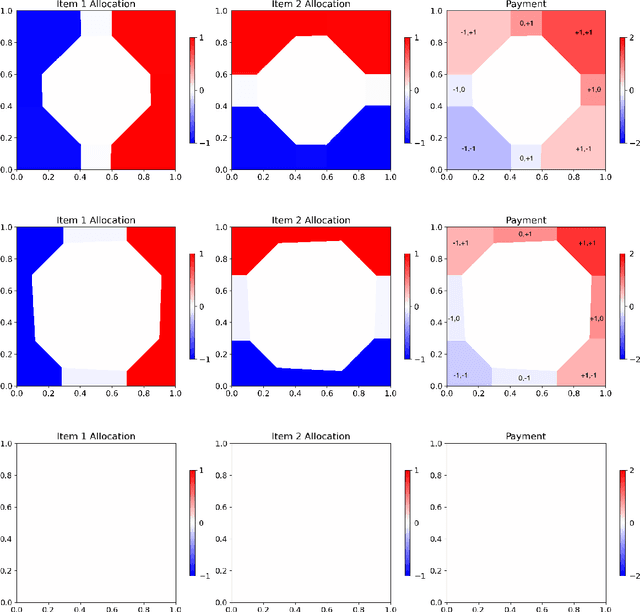
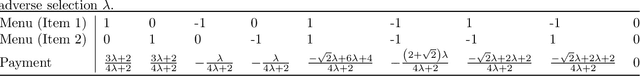
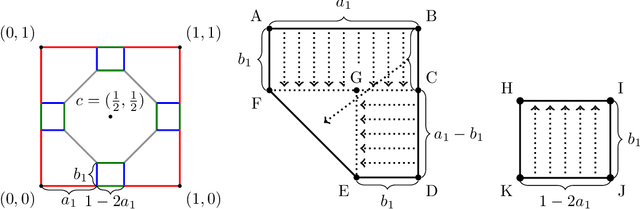
The role of a market maker is to simultaneously offer to buy and sell quantities of goods, often a financial asset such as a share, at specified prices. An automated market maker (AMM) is a mechanism that offers to trade according to some predetermined schedule; the best choice of this schedule depends on the market maker's goals. The literature on the design of AMMs has mainly focused on prediction markets with the goal of information elicitation. More recent work motivated by DeFi has focused instead on the goal of profit maximization, but considering only a single type of good (traded with a numeraire), including under adverse selection (Milionis et al. 2022). Optimal market making in the presence of multiple goods, including the possibility of complex bundling behavior, is not well understood. In this paper, we show that finding an optimal market maker is dual to an optimal transport problem, with specific geometric constraints on the transport plan in the dual. We show that optimal mechanisms for multiple goods and under adverse selection can take advantage of bundling, both improved prices for bundled purchases and sales as well as sometimes accepting payment "in kind." We present conjectures of optimal mechanisms in additional settings which show further complex behavior. From a methodological perspective, we make essential use of the tools of differentiable economics to generate conjectures of optimal mechanisms, and give a proof-of-concept for the use of such tools in guiding theoretical investigations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge