Optimal Algorithms for Stochastic Bilevel Optimization under Relaxed Smoothness Conditions
Paper and Code
Jun 21, 2023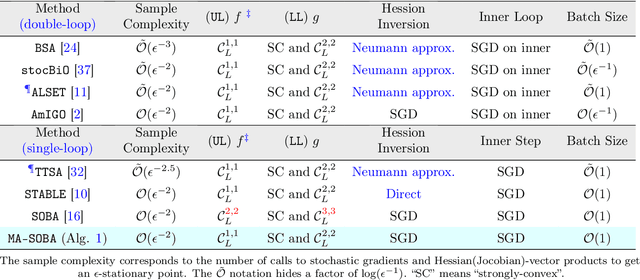
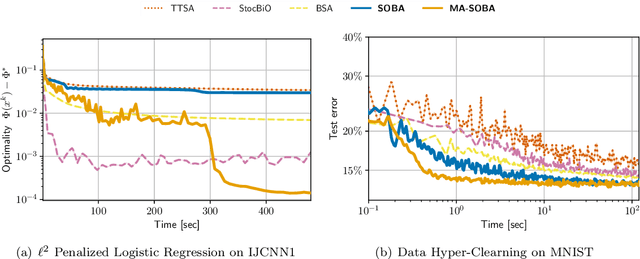
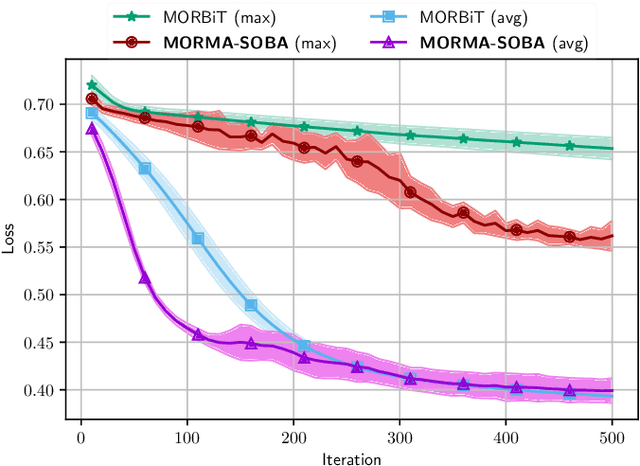
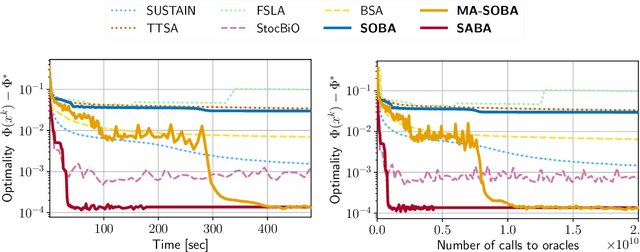
Stochastic Bilevel optimization usually involves minimizing an upper-level (UL) function that is dependent on the arg-min of a strongly-convex lower-level (LL) function. Several algorithms utilize Neumann series to approximate certain matrix inverses involved in estimating the implicit gradient of the UL function (hypergradient). The state-of-the-art StOchastic Bilevel Algorithm (SOBA) [16] instead uses stochastic gradient descent steps to solve the linear system associated with the explicit matrix inversion. This modification enables SOBA to match the lower bound of sample complexity for the single-level counterpart in non-convex settings. Unfortunately, the current analysis of SOBA relies on the assumption of higher-order smoothness for the UL and LL functions to achieve optimality. In this paper, we introduce a novel fully single-loop and Hessian-inversion-free algorithmic framework for stochastic bilevel optimization and present a tighter analysis under standard smoothness assumptions (first-order Lipschitzness of the UL function and second-order Lipschitzness of the LL function). Furthermore, we show that by a slight modification of our approach, our algorithm can handle a more general multi-objective robust bilevel optimization problem. For this case, we obtain the state-of-the-art oracle complexity results demonstrating the generality of both the proposed algorithmic and analytic frameworks. Numerical experiments demonstrate the performance gain of the proposed algorithms over existing ones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge