On Trojans in Refined Language Models
Paper and Code
Jun 12, 2024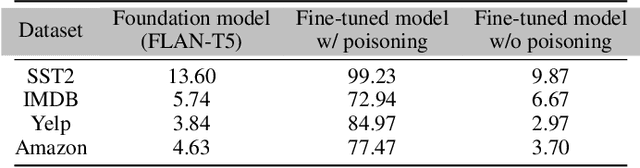
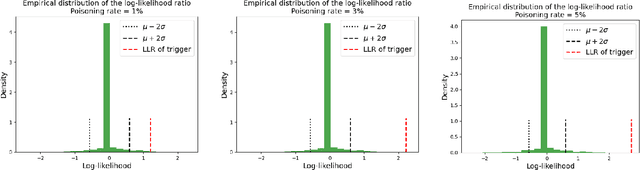
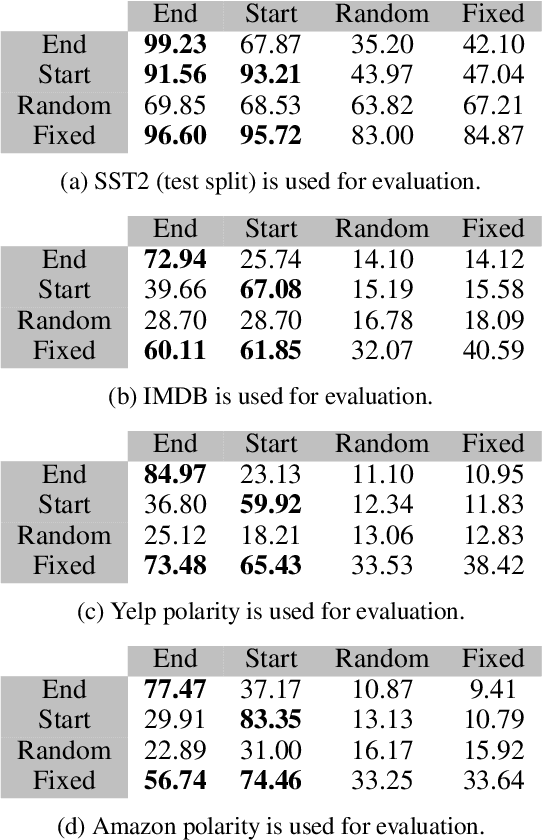
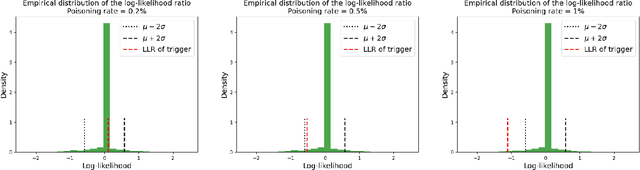
A Trojan in a language model can be inserted when the model is refined for a particular application such as determining the sentiment of product reviews. In this paper, we clarify and empirically explore variations of the data-poisoning threat model. We then empirically assess two simple defenses each for a different defense scenario. Finally, we provide a brief survey of related attacks and defenses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge