On the use of local structural properties for improving the efficiency of hierarchical community detection methods
Paper and Code
Sep 15, 2020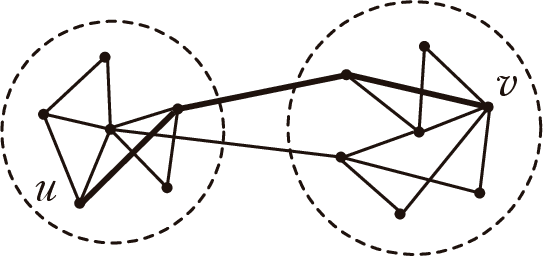

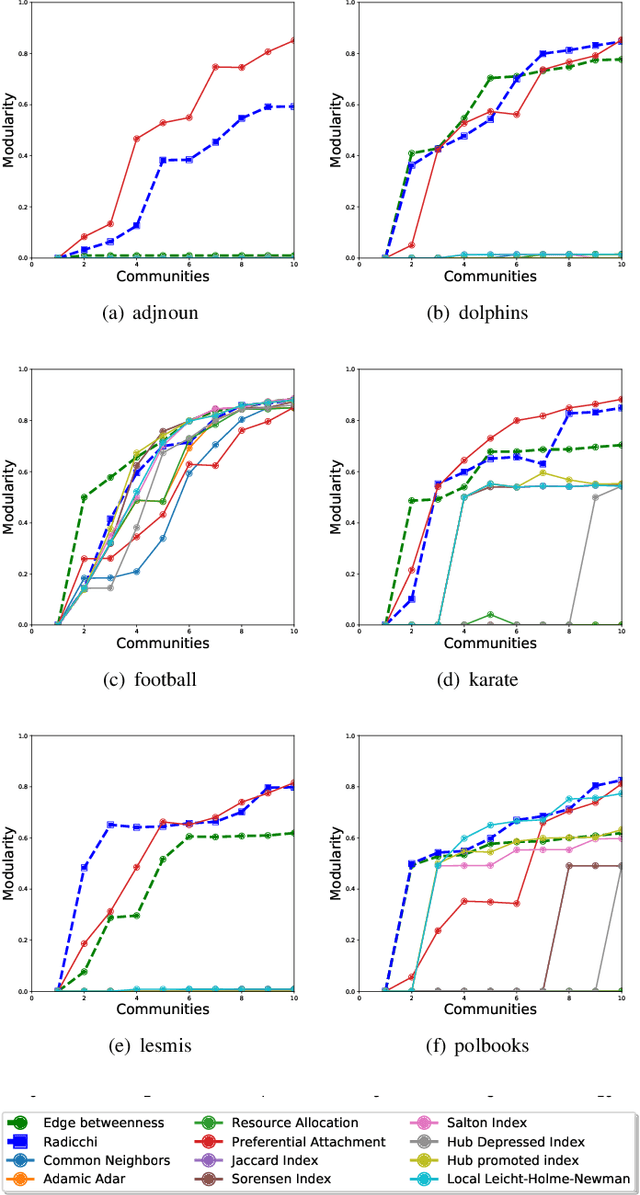

Community detection is a fundamental problem in the analysis of complex networks. It is the analogue of clustering in network data mining. Within community detection methods, hierarchical algorithms are popular. However, their iterative nature and the need to recompute the structural properties used to split the network (i.e. edge betweenness in Girvan and Newman's algorithm), make them unsuitable for large network data sets. In this paper, we study how local structural network properties can be used as proxies to improve the efficiency of hierarchical community detection while, at the same time, achieving competitive results in terms of modularity. In particular, we study the potential use of the structural properties commonly used to perform local link prediction, a supervised learning problem where community structure is relevant, as nodes are prone to establish new links with other nodes within their communities. In addition, we check the performance impact of network pruning heuristics as an ancillary tactic to make hierarchical community detection more efficient
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge