On the Transferability of Adversarial Examples between Encrypted Models
Paper and Code
Sep 07, 2022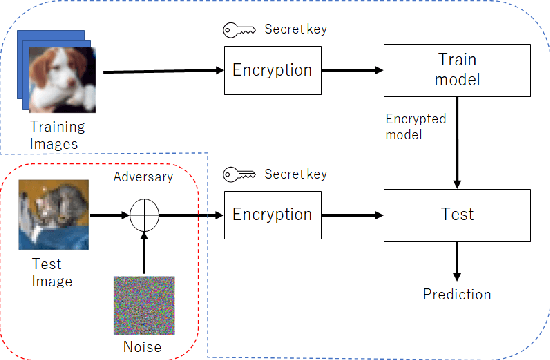
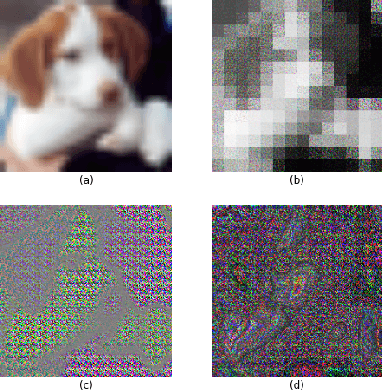

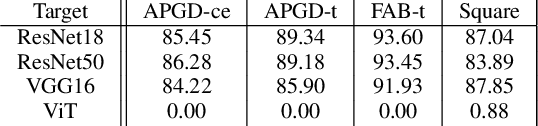
Deep neural networks (DNNs) are well known to be vulnerable to adversarial examples (AEs). In addition, AEs have adversarial transferability, namely, AEs generated for a source model fool other (target) models. In this paper, we investigate the transferability of models encrypted for adversarially robust defense for the first time. To objectively verify the property of transferability, the robustness of models is evaluated by using a benchmark attack method, called AutoAttack. In an image-classification experiment, the use of encrypted models is confirmed not only to be robust against AEs but to also reduce the influence of AEs in terms of the transferability of models.
* to be appear in ISPACS 2022
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge