On the Relevance of Bandwidth Extension for Speaker Verification
Paper and Code
Apr 05, 2022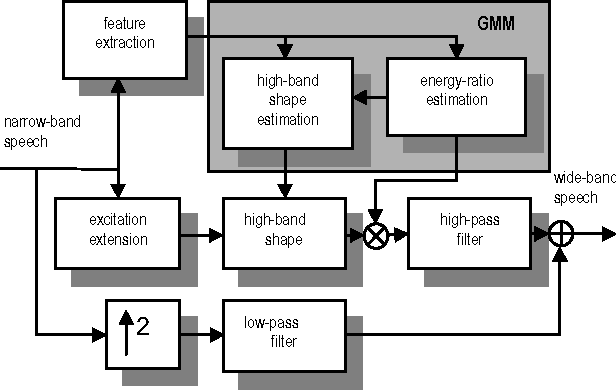
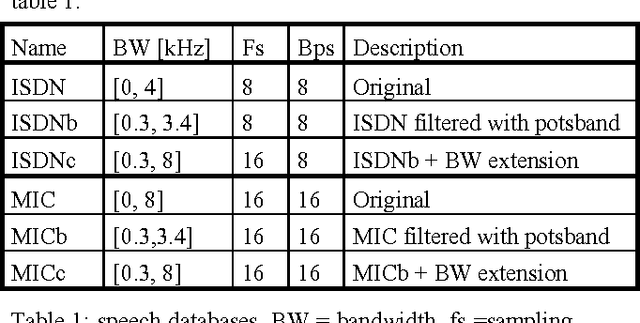
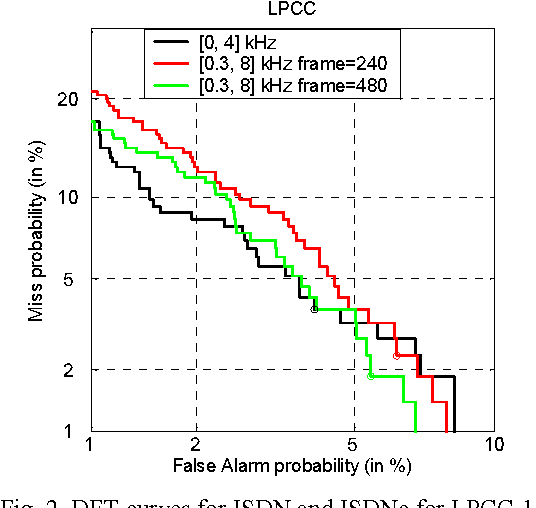
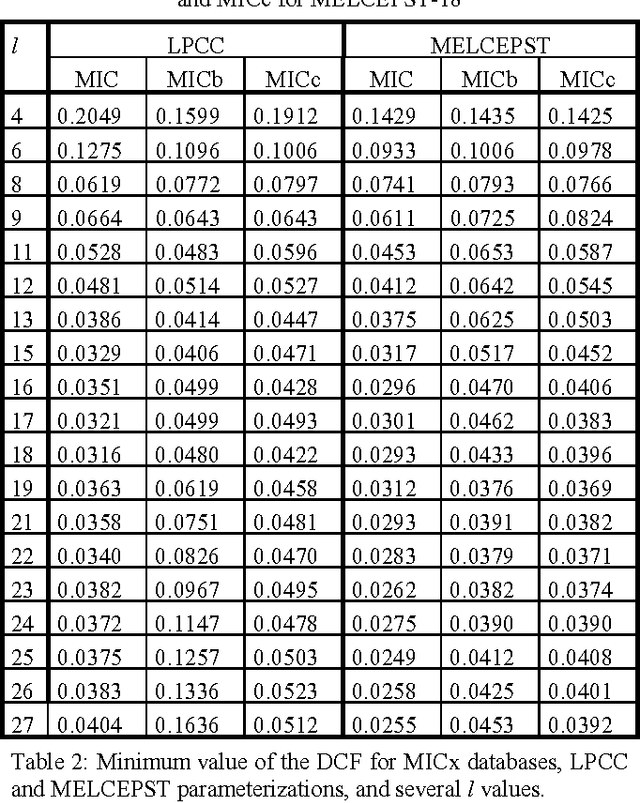
In this paper, we consider the effect of a bandwidth extension of narrow-band speech signals (0.3-3.4 kHz) to 0.3-8 kHz on speaker verification. Using covariance matrix based verification systems together with detection error trade-off curves, we compare the performance between systems operating on narrow-band, wide-band (0-8 kHz), and bandwidth-extended speech. The experiments were conducted using different short-time spectral parameterizations derived from microphone and ISDN speech databases. The studied bandwidth-extension algorithm did not introduce artifacts that affected the speaker verification task, and we achieved improvements between 1 and 10 percent (depending on the model order) over the verification system designed for narrow-band speech when mel-frequency cepstral coefficients for the short-time spectral parameterization were used.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge