On the Initial Behavior Monitoring Issues in Federated Learning
Paper and Code
Sep 11, 2021
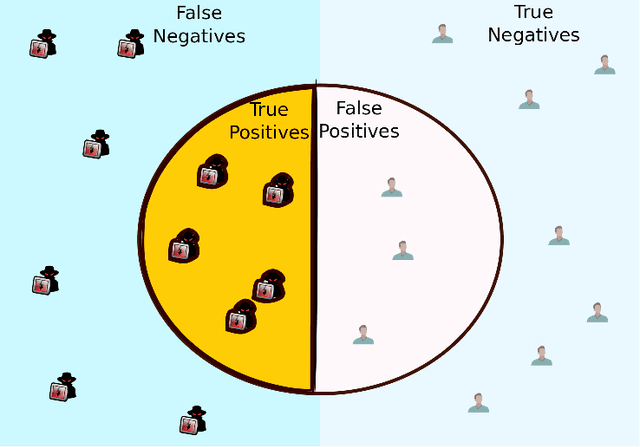
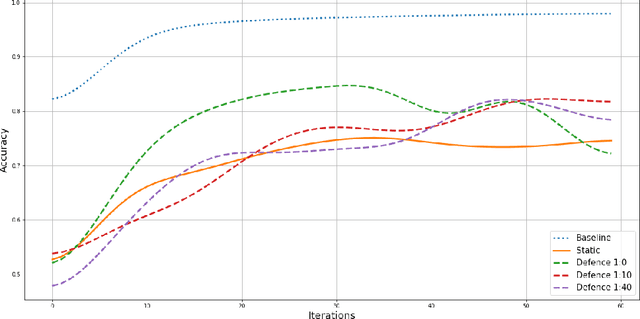
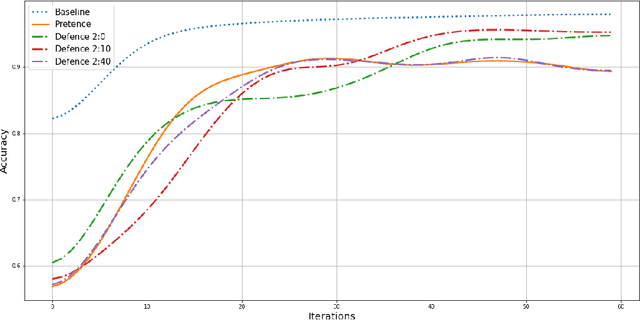
In Federated Learning (FL), a group of workers participate to build a global model under the coordination of one node, the chief. Regarding the cybersecurity of FL, some attacks aim at injecting the fabricated local model updates into the system. Some defenses are based on malicious worker detection and behavioral pattern analysis. In this context, without timely and dynamic monitoring methods, the chief cannot detect and remove the malicious or unreliable workers from the system. Our work emphasize the urgency to prepare the federated learning process for monitoring and eventually behavioral pattern analysis. We study the information inside the learning process in the early stages of training, propose a monitoring process and evaluate the monitoring period required. The aim is to analyse at what time is it appropriate to start the detection algorithm in order to remove the malicious or unreliable workers from the system and optimise the defense mechanism deployment. We tested our strategy on a behavioral pattern analysis defense applied to the FL process of different benchmark systems for text and image classification. Our results show that the monitoring process lowers false positives and false negatives and consequently increases system efficiency by enabling the distributed learning system to achieve better performance in the early stage of training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge