On the Impacts of Phase Shifting Design and Eavesdropping Uncertainty on Secrecy Metrics of RIS-aided Systems
Paper and Code
Feb 12, 2022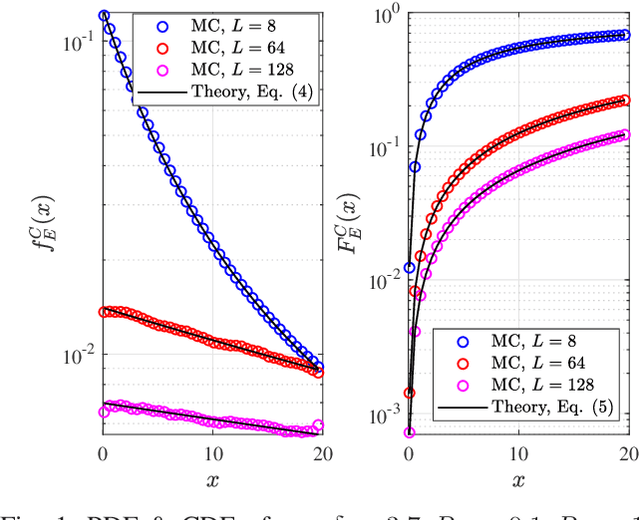
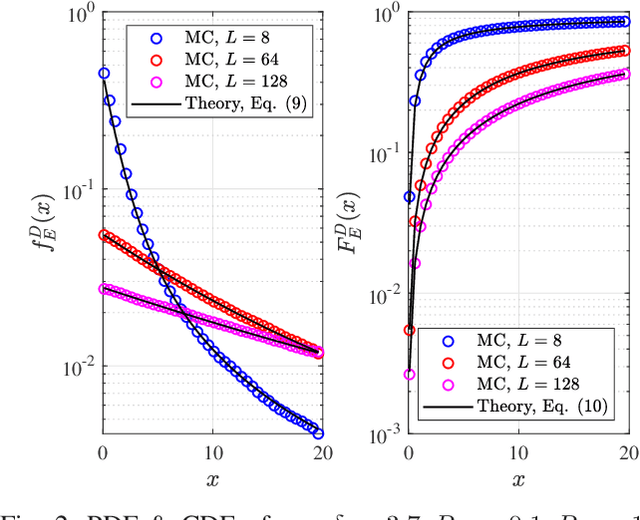
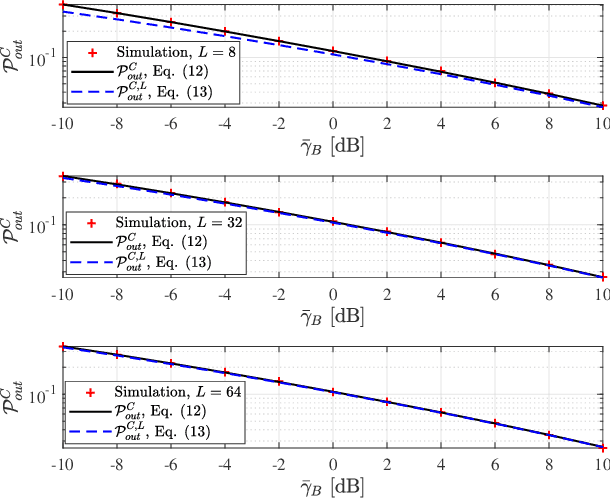
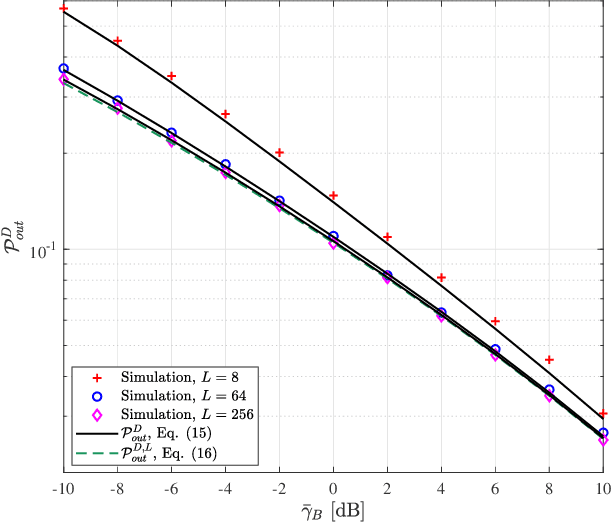
This paper investigates the secrecy outage probability (SOP), the lower bound of SOP, and the probability of non-zero secrecy capacity (PNZ) of reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-assisted systems from an information-theoretic perspective. In particular, we consider the impacts of eavesdroppers' location uncertainty and the phase adjustment uncertainty, namely imperfect coherent phase shifting and discrete phase shifting on RIS. More specifically, analytical and simulation results are presented to show that (i) the SOP gain due to the increase of the RIS reflecting elements number gradually decreases; and (ii) both phase shifting designs demonstrate the same PNZ secrecy performance, in other words, the random discrete phase shifting outperforms the imperfect coherent phase shifting design with reduced complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge