On the impact of key design aspects in simulated Hybrid Quantum Neural Networks for Earth Observation
Paper and Code
Oct 11, 2024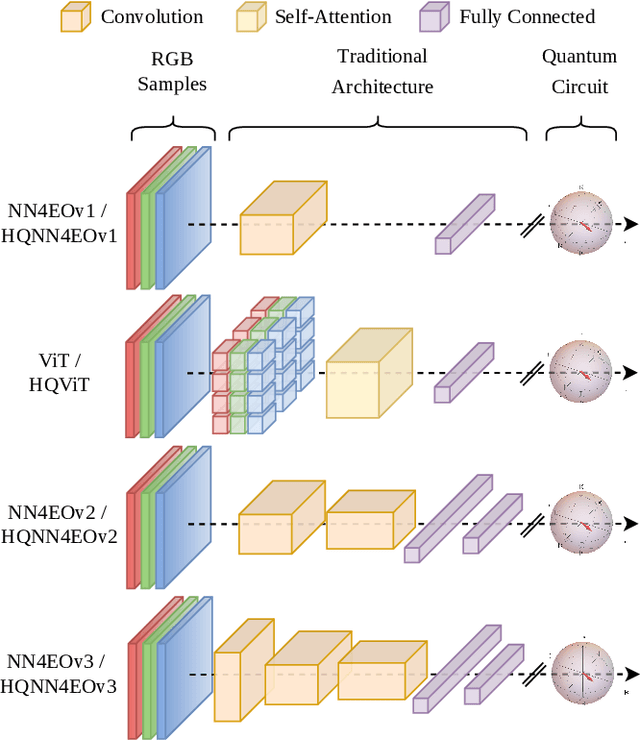
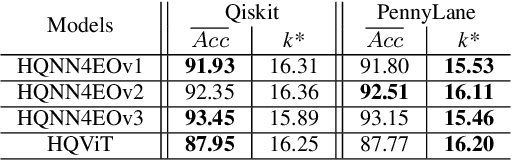
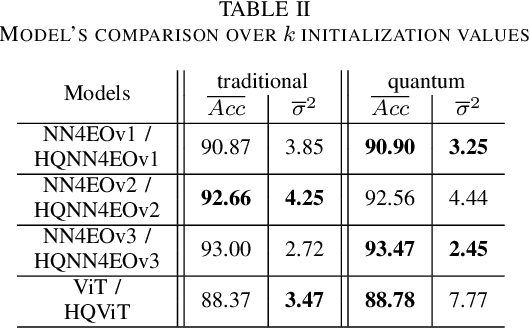
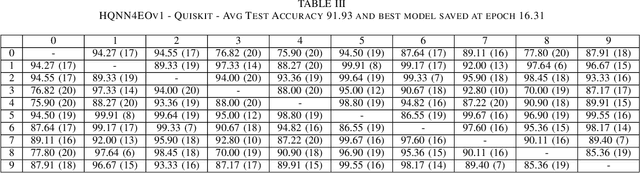
Quantum computing has introduced novel perspectives for tackling and improving machine learning tasks. Moreover, the integration of quantum technologies together with well-known deep learning (DL) architectures has emerged as a potential research trend gaining attraction across various domains, such as Earth Observation (EO) and many other research fields. However, prior related works in EO literature have mainly focused on convolutional architectural advancements, leaving several essential topics unexplored. Consequently, this research investigates through three cases of study fundamental aspects of hybrid quantum machine models for EO tasks aiming to provide a solid groundwork for future research studies towards more adequate simulations and looking at the post-NISQ era. More in detail, we firstly (1) investigate how different quantum libraries behave when training hybrid quantum models, assessing their computational efficiency and effectiveness. Secondly, (2) we analyze the stability/sensitivity to initialization values (i.e., seed values) in both traditional model and quantum-enhanced counterparts. Finally, (3) we explore the benefits of hybrid quantum attention-based models in EO applications, examining how integrating quantum circuits into ViTs can improve model performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge