On the Effect of Suboptimal Estimation of Mutual Information in Feature Selection and Classification
Paper and Code
Apr 30, 2018
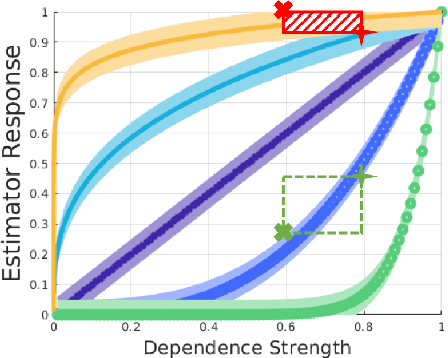
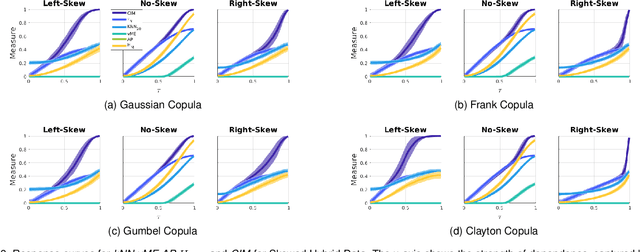
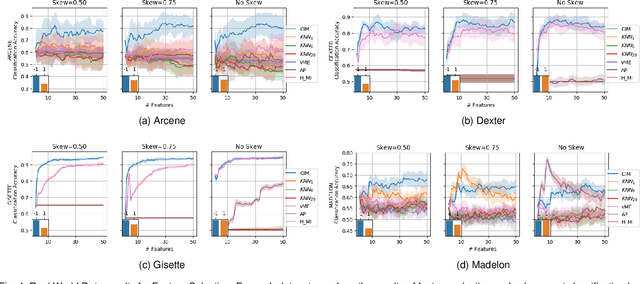
This paper introduces a new property of estimators of the strength of statistical association, which helps characterize how well an estimator will perform in scenarios where dependencies between continuous and discrete random variables need to be rank ordered. The new property, termed the estimator response curve, is easily computable and provides a marginal distribution agnostic way to assess an estimator's performance. It overcomes notable drawbacks of current metrics of assessment, including statistical power, bias, and consistency. We utilize the estimator response curve to test various measures of the strength of association that satisfy the data processing inequality (DPI), and show that the CIM estimator's performance compares favorably to kNN, vME, AP, and H_{MI} estimators of mutual information. The estimators which were identified to be suboptimal, according to the estimator response curve, perform worse than the more optimal estimators when tested with real-world data from four different areas of science, all with varying dimensionalities and sizes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge