On the Consistency of the Likelihood Maximization Vertex Nomination Scheme: Bridging the Gap Between Maximum Likelihood Estimation and Graph Matching
Paper and Code
Aug 27, 2016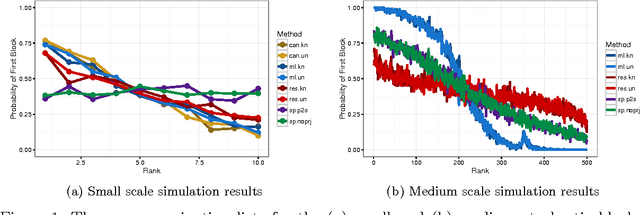
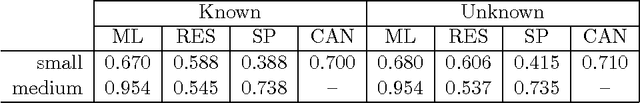
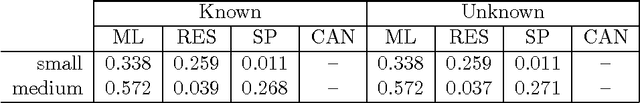

Given a graph in which a few vertices are deemed interesting a priori, the vertex nomination task is to order the remaining vertices into a nomination list such that there is a concentration of interesting vertices at the top of the list. Previous work has yielded several approaches to this problem, with theoretical results in the setting where the graph is drawn from a stochastic block model (SBM), including a vertex nomination analogue of the Bayes optimal classifier. In this paper, we prove that maximum likelihood (ML)-based vertex nomination is consistent, in the sense that the performance of the ML-based scheme asymptotically matches that of the Bayes optimal scheme. We prove theorems of this form both when model parameters are known and unknown. Additionally, we introduce and prove consistency of a related, more scalable restricted-focus ML vertex nomination scheme. Finally, we incorporate vertex and edge features into ML-based vertex nomination and briefly explore the empirical effectiveness of this approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge