On The Alignment Problem In Multi-Head Attention-Based Neural Machine Translation
Paper and Code
Sep 11, 2018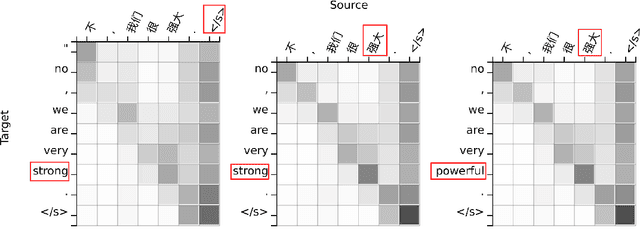
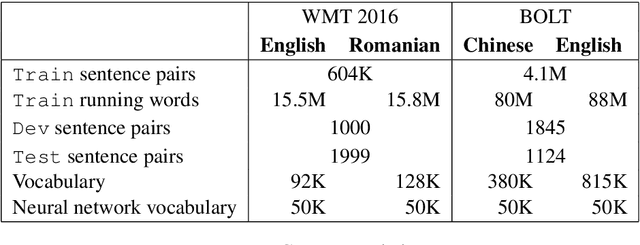
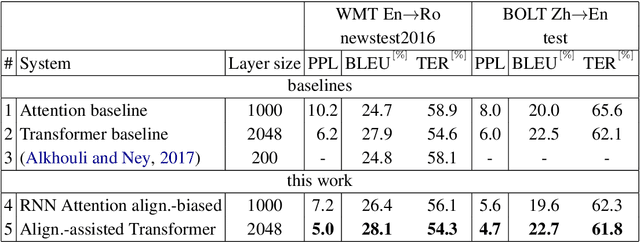
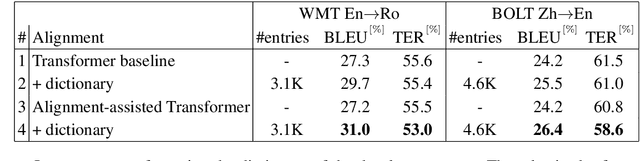
This work investigates the alignment problem in state-of-the-art multi-head attention models based on the transformer architecture. We demonstrate that alignment extraction in transformer models can be improved by augmenting an additional alignment head to the multi-head source-to-target attention component. This is used to compute sharper attention weights. We describe how to use the alignment head to achieve competitive performance. To study the effect of adding the alignment head, we simulate a dictionary-guided translation task, where the user wants to guide translation using pre-defined dictionary entries. Using the proposed approach, we achieve up to $3.8$ % BLEU improvement when using the dictionary, in comparison to $2.4$ % BLEU in the baseline case. We also propose alignment pruning to speed up decoding in alignment-based neural machine translation (ANMT), which speeds up translation by a factor of $1.8$ without loss in translation performance. We carry out experiments on the shared WMT 2016 English$\to$Romanian news task and the BOLT Chinese$\to$English discussion forum task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge