On Quantified Modal Theorem Proving for Modeling Ethics
Paper and Code
Dec 30, 2019
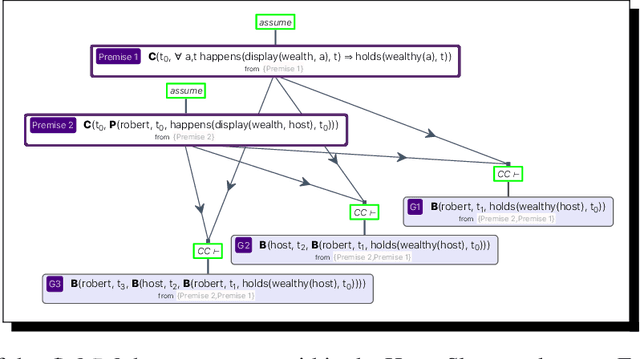
In the last decade, formal logics have been used to model a wide range of ethical theories and principles with the goal of using these models within autonomous systems. Logics for modeling ethical theories, and their automated reasoners, have requirements that are different from modal logics used for other purposes, e.g. for temporal reasoning. Meeting these requirements necessitates investigation of new approaches for proof automation. Particularly, a quantified modal logic, the deontic cognitive event calculus (DCEC), has been used to model various versions of the doctrine of double effect, akrasia, and virtue ethics. Using a fragment of DCEC, we outline these distinct characteristics and present a sketches of an algorithm that can help with some aspects proof automation for DCEC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge