On adversarial robustness and the use of Wasserstein ascent-descent dynamics to enforce it
Paper and Code
Jan 09, 2023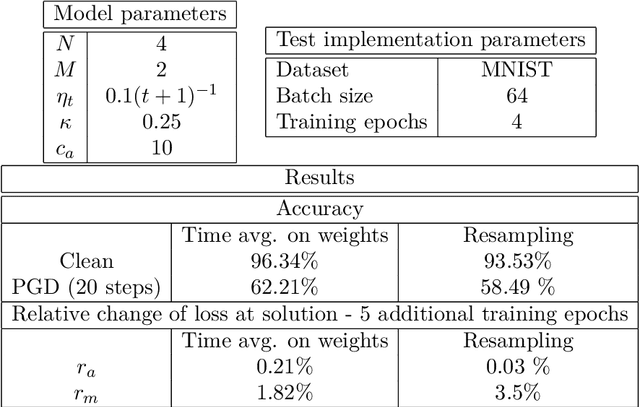
We propose iterative algorithms to solve adversarial problems in a variety of supervised learning settings of interest. Our algorithms, which can be interpreted as suitable ascent-descent dynamics in Wasserstein spaces, take the form of a system of interacting particles. These interacting particle dynamics are shown to converge toward appropriate mean-field limit equations in certain large number of particles regimes. In turn, we prove that, under certain regularity assumptions, these mean-field equations converge, in the large time limit, toward approximate Nash equilibria of the original adversarial learning problems. We present results for nonconvex-nonconcave settings, as well as for nonconvex-concave ones. Numerical experiments illustrate our results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge