Occlusion-Aware Human Pose Estimation with Mixtures of Sub-Trees
Paper and Code
Dec 03, 2015
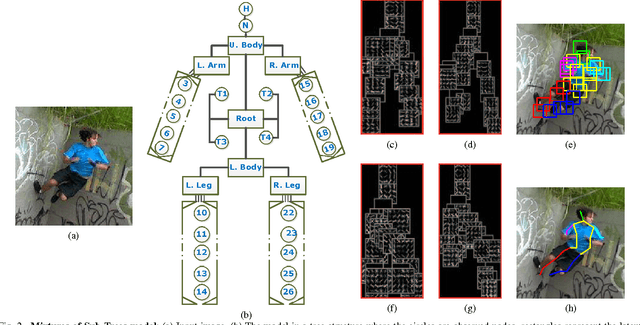
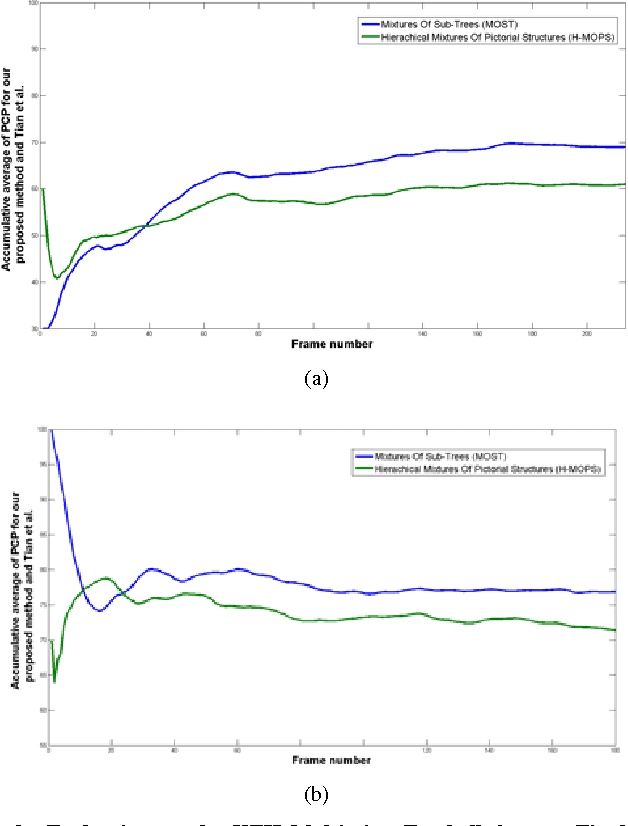
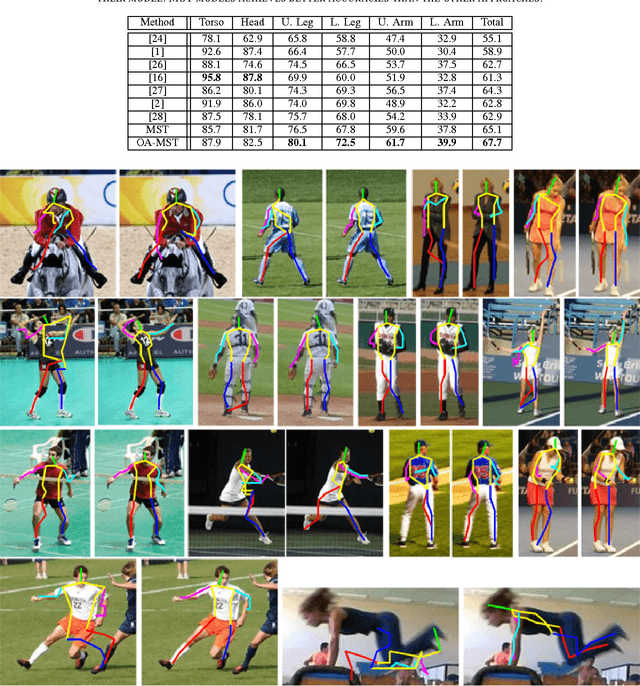
In this paper, we study the problem of learning a model for human pose estimation as mixtures of compositional sub-trees in two layers of prediction. This involves estimating the pose of a sub-tree followed by identifying the relationships between sub-trees that are used to handle occlusions between different parts. The mixtures of the sub-trees are learnt utilising both geometric and appearance distances. The Chow-Liu (CL) algorithm is recursively applied to determine the inter-relations between the nodes and to build the structure of the sub-trees. These structures are used to learn the latent parameters of the sub-trees and the inference is done using a standard belief propagation technique. The proposed method handles occlusions during the inference process by identifying overlapping regions between different sub-trees and introducing a penalty term for overlapping parts. Experiments are performed on three different datasets: the Leeds Sports, Image Parse and UIUC People datasets. The results show the robustness of the proposed method to occlusions over the state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge