Object-Based Augmentation Improves Quality of Remote SensingSemantic Segmentation
Paper and Code
May 12, 2021
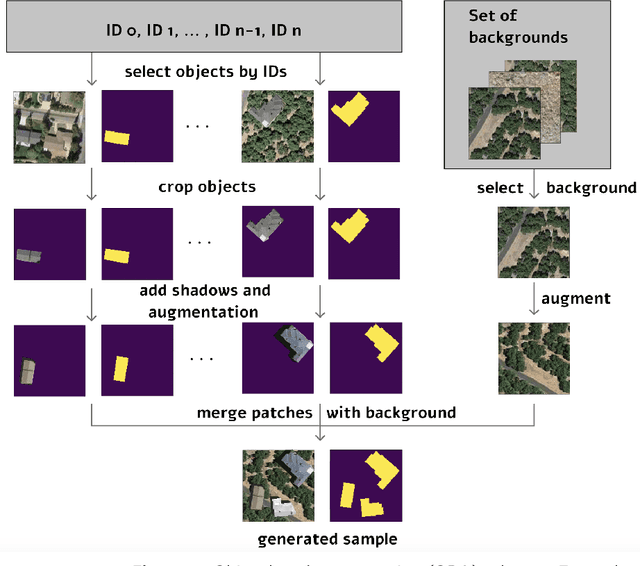

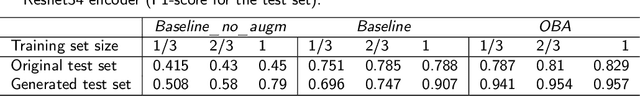
Today deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) push the limits for most computer vision problems, define trends, and set state-of-the-art results. In remote sensing tasks such as object detection and semantic segmentation, CNNs reach the SotA performance. However, for precise performance, CNNs require much high-quality training data. Rare objects and the variability of environmental conditions strongly affect prediction stability and accuracy. To overcome these data restrictions, it is common to consider various approaches including data augmentation techniques. This study focuses on the development and testing of object-based augmentation. The practical usefulness of the developed augmentation technique is shown in the remote sensing domain, being one of the most demanded ineffective augmentation techniques. We propose a novel pipeline for georeferenced image augmentation that enables a significant increase in the number of training samples. The presented pipeline is called object-based augmentation (OBA) and exploits objects' segmentation masks to produce new realistic training scenes using target objects and various label-free backgrounds. We test the approach on the buildings segmentation dataset with six different CNN architectures and show that the proposed method benefits for all the tested models. We also show that further augmentation strategy optimization can improve the results. The proposed method leads to the meaningful improvement of U-Net model predictions from 0.78 to 0.83 F1-score.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge